8.9. CSS Layout Tutorial In this tutorial, you'll build a basic two-column page design using nothing but Cascading Style Sheets (Figure 8-20 shows the final product). In the process, you'll use Dreamweaver 8's CSS tools, marvel at Dreamweaver's improved display, and learn how to use the program's layer tools. 8.9.1. Getting Started Before you begin building the page, download the tutorial files. As always, you'll find them at www.sawmac.com/dw8. Click the Tutorials link to go to the tutorials page and then click the link to the Layout Tutorial. When the files have downloaded and decompressed, you should have a folder named DWLayout on your computer, containing the Web pages and graphics needed for this tutorial. If you're having difficulties, the Web site contains detailed instructions for downloading the files you'll be using with this book. -
In Dreamweaver, choose Site  New Site . New Site . The Site Definition window appears. Make sure the Advanced tab is selected. (The Basic tab offers a simpler, wizard-based approach to setting up sites, but once you've got the handle on setting up sites, it's just too slow. The Site Definition wizard's discussed on Section 1.3.2.) -
In the Site Name field, type Layout Tutorial . This is the name that Dreamweaver uses while you're working on this tutorial. -
Click the folder icon next to the label "Local root folder." The Choose Local Root Folder window opens. -
Browse to and select the DWLayout folder . Windows and Macs handle this step slightly differently, as described on Section 1.3.2. Selecting the DWLayout folder makes it the local root folderthe folder that holds all the files, graphics, and other folders that are part of a single Web site (see Section 1.3.1). -
Click the OK button . Dreamweaver reads the files in the folder and displays them in the Files panel. Now you're all set to begin the tutorial. 8.9.2. Adding a Banner Layer So you can get right down to the fun of laying out a page with Cascading Style Sheets, you'll start with a partly finished page, complete with content and some basic CSS styles for text formatting. Now you'll add the layers that control the layout of the page: -
Choose File  Open and, in the DWLayout folder, select the file named layout.html . Open and, in the DWLayout folder, select the file named layout.html . Alternatively, open the Files panel (Windows  Files) and double-click the file layout.html to open it. This page is a headline story for the National Exasperator Web site. You'll notice that there's no layout, just content that runs from the top to the bottom of the page in the generic, ho-hum style of HTML. You'll create several CSS styles to position the banner, sidebar, and main content areas of the page. Files) and double-click the file layout.html to open it. This page is a headline story for the National Exasperator Web site. You'll notice that there's no layout, just content that runs from the top to the bottom of the page in the generic, ho-hum style of HTML. You'll create several CSS styles to position the banner, sidebar, and main content areas of the page. -
Make sure the CSS Styles panel's open (Window  CSS Styles) and click the New Style button (see Figure 6-1) . CSS Styles) and click the New Style button (see Figure 6-1) . You'll start by creating a layer for the page's banner. -
Click the Advanced button and, in the Selector box, type #banner . You're creating an ID style, an advanced style that always begins with a #. You'll also add this style to a new external style sheet file. -
From the "Define in" menu, select New Style Sheet File (see Figure 8-13) . There's already one external style sheet attached to this page, called global_styles.css . You could add these layer styles to that file, but for this tutorial, you'll see you can have multiple external style sheets attached to a single page. Figure 8-13. You can have more than one external style sheet per page. For example, you can create a separate style sheet for form elements. That way, you only need to include that style sheet for pages that actually include forms.  -
Click OK. In the Save Style Sheet File As box, type layout.css in the File Name field (Save As field on a Mac). Click Save . Dreamweaver saves a new CSS file into your site and opens the CSS Rule Definition window. You'll start by adding a background property. -
Click the Background category, and then click the Browse button to the right of the Background Image box . This opens the now-familiar Select Image Source window for selecting graphic files. You're going to add a red stripe (just like in last chapter's tutorial) that extends from the logo to the right edge of the page, giving the illusion of one really wide graphic. -
Navigate to the Images Global folder and double-click the bg_banner.gif file . Because background images normally tile left to right and top to bottom, you're going to add instructions to this style so the stripe only tiles horizontally across the page. -
Choose "repeat-x" from the Repeat menu. Click Positioning in the Category list . Dreamweaver displays all of the CSS Positioning propertiesthe heart of creating absolutely positioned elements. Here's where the magic is. -
From the Type menu, select "absolute" . This gives the layer an absolute position on the page. Because the banner stretches across the browser windowno matter what size that browser window isyou'll next give the layer a width that spreads across the page. -
Type 100 in the Width box and select % from the menu next to it . You've just set the layer to 100 percent width, meaning it takes up 100 percent of the available space in the browser. Next, you'll position the layer in the top-left corner of the page.
Tip: There's a shortcut for typing values into a CSS box. Instead of typing a number in one box and then selecting a unit of measurement (pixels, percentages, or ems) from a menu, you can type the number and measurement together in the first box: 100% , for example, or 1em , or 20px . Dreamweaver automatically adjusts the units menu.Just don't put a space between the number and the measurement type. For example, 20 px won't work.
-
For the Placement options, type in the Top box and in the Left box . The window should now look like Figure 8-14. -
Click OK to finish creating the style . You've just created your first ID style. Congratulations. Applying it is a piece of cake. Figure 8-14. The Positioning properties in the CSS Rule Definition window provide all the options you need to create absolutely positioned layers. 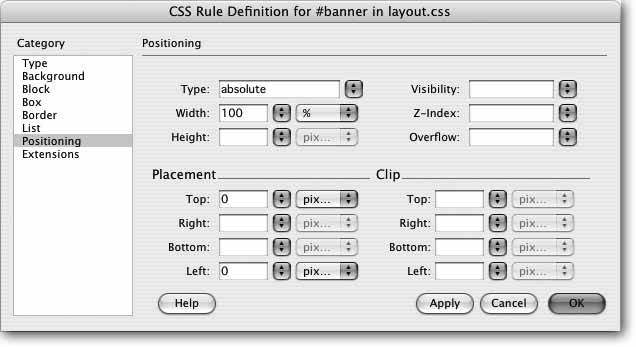 -
Select the National Exasperator logo graphic, and choose Insert  Layout Objects Layout Objects  Div Tag . Div Tag . Alternatively you can click the Insert Div Tag object on the Layout tab of the Insert bar (see Figure 8-5). Either way, the Insert Div Tag window opens. -
From the ID menu, select "banner." Make sure the "Wrap around selection" option's turned on, and click OK . Dreamweaver wraps the new layer around the graphic. The banner moves to the top-left corner of the page, and the logo appears to extend the entire width of the window (see top image in Figure 8-15). In the next part of this tutorial, you'll create a layer to position the sidebar info on the left edge of the page below the banner. Figure 8-15. The Layers panel can temporarily hide a layer that's getting in the way. It's easy to remove the National Exasperator banner in the top window; just click the eyeball icon on the Layers panel, and the banner disappears (bottom). When you're finished with your design, you can make the layer visible again. 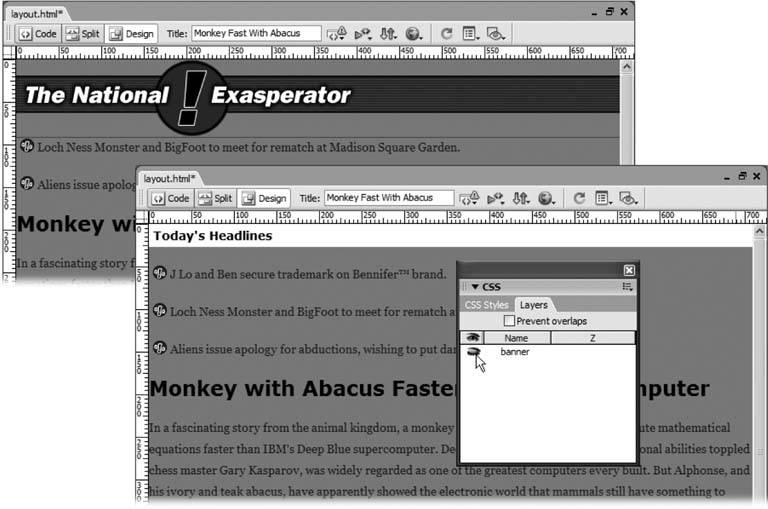
8.9.3. Creating the Sidebar You may have noticed something strange after you added that banner layer. The rest of the text on the page moved up, and much of the sidebar information"Today's Headlines"disappeared underneath the banner. Welcome to absolute positioning and CSS-based layout! As described on Section 8.3.1, whenever you use absolute positioning, the content in the layer is moved out of the normal flow of the page. In this case, the banner floats above the page, and the other content fills in the leftover space. It's as if the sidebar information and other page content don't know the layer even exists. In this next phase, you'll format the sidebar so that it fits below the banner, and you'll use some of Dreamweaver's tools for working with layers. First, you'll use the Layers panel to temporarily hide the banner as you format the other parts of the page: -
Choose Window  Layers to open the Layers panel . Layers to open the Layers panel . The Layers panel lets you hide layers and change their layering (how a layer overlaps another layer). In this case, you'll temporarily make the banner invisible so you can work on the sidebar. -
In the Layers panel, click to the left of the word "banner" (see Figure 8-15, bottom) . You should see a closed eye appear in this column. This indicates that the layer is now invisible, and the banner should disappear from the page. If you still see the banner, keep clicking in the Layers panel until the closed eye appears. Now you can see all of the content for the sidebar. It's a simple process to create a layer for that. -
In the Design panel groupwhere the Layers panel is locatedclick the CSS Styles tab to bring that panel to the front . Alternatively, you can choose Window  "CSS Styles panel to open the panel. "CSS Styles panel to open the panel. -
Click the New CSS Rule button to open the New CSS Rule window . Again, you'll create an ID style. -
Click the Advanced selector button and, in the Selector name box, type #sidebar . The "Define in" menu should say layout.css . Click OK to begin creating the style . This is another ID style that you'll store in the external style sheet you created earlier. You'll add some CSS properties to position this layer precisely on the screen. -
In the CSS Rule Definition window, click the Positioning category . This is the same process you used when creating the banner; however, you'll position the sidebar in a different location on the screen. -
From the position menu, select "absolute." The sidebar fills only a small part of the total width of the page, so set a pixel value for its width. -
In the width box, type 150 . Dreamweaver defaults to pixel values, so you don't have to do anything else with the width. However, you do want to position the layer so it's below the banner. -
For the Placement options, type 150 in the Top box and in the Left box . This places the sidebar 150 pixels down from the top of the page, but keeps it clinging to the left edge. -
Click OK to finish the style . Next, you'll select the sidebar content and wrap it in the layer. -
Click just before the letter T in "Today's Headlines" and drag down and to the right until you've selected the headline and the three bulleted items below it . -
Choose Insert  Layout Objects Layout Objects  Div Tag . Div Tag . Alternatively, you can click the Insert Div Tag object on the Layout tab of the Insert bar (see Figure 8-5). Either way, the Insert Div Tag window opens. -
From the ID menu, select "sidebar." Make sure the "Wrap around selection" option is turned on, and click OK . Dreamweaver wraps the new layer around the sidebar content. As with the banner, the sidebar is now taken out of the normal flow of the page, so the story text moves to the top of the page and flows under the sidebar. Don't worry; you'll fix that next. 8.9.4. Positioning the Main Content The main content for this pagethe story about the calculating monkeyshould go below the banner and to the right of the sidebar. It won't have a set width, however. Like the banner, the content should be fluid, so that if someone resizes his browser window, the story grows or shrinks to fit the available space. (This is like the "liquid HTML" table designs described on Section 7.3.6.) Using absolute positioning, it's difficult to get that kind of fluid design to work across all of today's browsers. Fortunately, there's a simple trick you can use to achieve the same goal: Instead of absolutely positioning the story content, you'll use large top and left margins to actually indent the story area away from the banner and sidebar. This is a common trick used by many Web designers who employ CSS-based layout. Here's how it works: -
In the CSS Styles panel, click the New Rule button . You'll create another ID style next. -
In the New CSS Rule window, create an ID style named #main for the layout.css style sheet. Click OK . Refer to step 5 in the previous section for more detail on this process. -
In the CSS Rule Definition window, click the Box category . You'll set the margin properties here. -
Turn off the "Same for all" box under the Margin heading; type 115 in the Top box, type 175 in the Left box, and type 10 in the Right box (see Figure 8-16) . This indents the content 115 pixels from the top of the page and 175 pixels from the left edge. The 10 pixel value in the Right box moves the text away from the right edge so it doesn't collide with the edge of the browser window. Note that you're not using absolute positioning for this style. In other words, you're not creating a layer here, just indenting the text as you might with any CSS style you create. It just so happens that the margins you're adding are so large, they effectively position the text out of the way of the banner and sidebar. You're also going to add a jazzy border along the left edge of the text, so you need to add a bit of padding to move the text away from the border. Figure 8-16. Margin properties offer another way to place elements on a page by letting you indent content away from absolutely positioned elements on a page. This is particularly useful for parts of a pagelike the main textthat need to change size based on the width of a visitor's browser window. 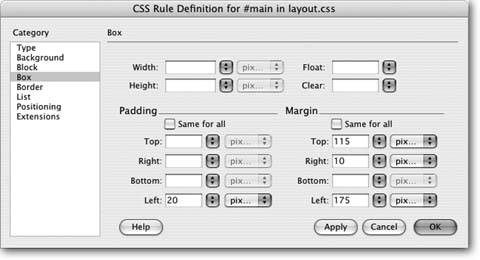 -
Turn off the "Same for all" box underneath the Padding heading and, in the Left box, type 20 . The CSS Rule Definition window should look like Figure 8-16. Finally, you'll add a border to this style. -
In the Category list, click Border . You'll add a border only to the left edge of the text. -
Turn off all three "Same for all" boxes, and use the following three values for the Left border settings: dotted for the style, 2 pixels for the width, and a color of white (#FFFFFF) . This creates a 2-pixel dotted white border along the left edge of the main content. -
Click OK to create the style . You apply this style just like all the others. -
Click before the letter "M" in Monkey and drag down and to the right to select all of the text for the story . You won't select the sidebar doing this. Even though the sidebar appears to be inside that text, its code is actually at the top of the page. -
Finally, repeat steps 12 and 13 on Section 8.9.4 to wrap this text with the style you just created . The page is coming together nicely . You'll just make the banner visible again so you can see the page in all its glory . -
Choose Window  Layers to open the Layers panel. Click the closed eye icon to the left of the banner layer until the banner appears on the page again . Layers to open the Layers panel. Click the closed eye icon to the left of the banner layer until the banner appears on the page again . You can either click until you see an open-eye iconmeaning the layer's visibleor until you see no icon (the default setting, which is also visible). In the last part of this tutorial, you'll fine-tune your design and add a navigation bar. 8.9.5. Fine-Tuning the Design The page is looking pretty good. You've placed different elements in different parts of the pagewithout tables! However, it could use a little adjustment. The side-bar's a tad too low on the page, and the banner needs a navigation bar: -
In the document window, move your mouse over the top edge of the sidebar until the cursor changes appearance. Click to select the layer . You can also select a layer by clicking any of its edges, selecting the layer's name in the Layers panel, or by clicking the layer's selection handle (see Figure 8-7). -
Grab anywhere on the top edge of the layer, except any of the resize handles, and drag up until the top of the layer overlaps the banner by a couple of pixels (see Figure 8-17) . Notice that you can actually put this layer on top of the bannersomething you can't do with normal HTML. The exact placement isn't importantwhatever looks good to you. After testing the design in a browser, you can always return and change its placement. Dragging either the top or bottom resize handle sets a height for the layer. In this case, you don't want to do that. Since you don't know how many headlines you may have listed at a time, you'll never know the exact height. Better to let the Web browser just resize the layer automatically based on the content inside it.
Note: You may notice that if you make a mistakedrag the layer off the left edge of the page, for exampleyou can't use Edit  Undo to get the layer back to its original position. Thats because you're not actually changing the Web page; you're altering the CSS in the external stylesheet: layout .css. That file has to be opened, and you have to switch to it, to undo any changes you make to a layer by dragging it around the page. Undo to get the layer back to its original position. Thats because you're not actually changing the Web page; you're altering the CSS in the external stylesheet: layout .css. That file has to be opened, and you have to switch to it, to undo any changes you make to a layer by dragging it around the page.
Figure 8-17. You can use Dreamweaver's WYSIWYG layer-editing tools to change the position, width, height, and other layer properties. When you resize a layer by dragging one of the resize handles, Dreamweaver updates the CSS style for the layereven if the CSS information is in an external style sheet! Also, if you hover over a selected layer, Dreamweaver 8 provides a quick overview of the style name and any relevant positioning properties in a yellow pop-up box, as shown here.  -
With the layer still selected, type 177px into the Width box in the Property inspector . This makes the layer 177 pixels widejust wide enough to touch the white border on the left edge of the main content. Of course, you could have used the right resize handle to make this layer wider. Dreamweaver provides many ways to do the same thing.
Note: You may notice that resize handles never appear around the main content of this page. Dreamweaver includes resize handles only for absolutely positioned elementswhat Dreamweaver calls layers . Because you used a little trick to position the main contentsetting the Margin propertiesyou can't resize this part of the page like you can the layers. If you want to move the main content higher on the page, or farther to the right, you have to adjust the Margin properties of its style.
In the last part of this tutorial, you'll add a navigation bar to the banner. -
Choose Window  CSS Styles to open the CSS Styles panel. Click the New CSS Rule button . CSS Styles to open the CSS Styles panel. Click the New CSS Rule button . You'll create another layer to hold the site's navigation buttons . -
As with the previous layers, create an ID style named #nav in the layout.css style sheet. Click OK . This process is detailed in steps 4 and 5 on Section 8.9.3. -
In the CSS Rule Definition window, click the Positioning category and enter the values shown in Figure 8-18 . In essence, you're creating an absolutely positioned layer that's 455 pixels wide and appears 65 pixels from the top and 251 pixels from the left. Figure 8-18. To accurately place an element on a page, you only need two placement settingsTop and Leftto specify where the layer's top and left edges appear on the page. 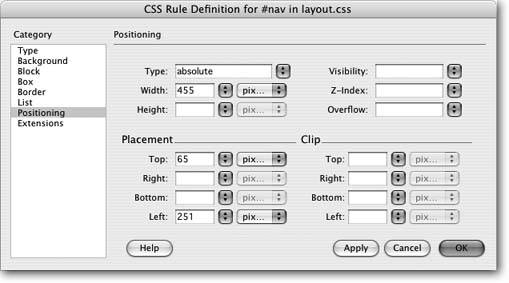 -
Click OK to create the style . This time, instead of wrapping already existing content with a layer, you'll insert the layer and then add content to it. -
Choose Insert  Layout Objects Layout Objects  Div Tag . Div Tag . Again, you can also use the Insert Div Tag object on the Layout tab of the Insert bar. Either way, the Insert Div Tag window appears (see Figure 8-19). -
Select "Before end of tag" and <div id="banner"> from the two Insert menus . Select "nav" from the ID menu (see Figure 8-19) . This series of steps inserts the new layer. However, instead of wrapping it around something, or even just dropping the layer on the page, you're inserting the layer inside the banner layer. This is called nesting a layer and has the benefit of making the navigation-bar layer a part of the banner. If you move the banner layersay, you want it a few pixels farther down on the screenthe navigation bar moves along with it.
Note: This example demonstrates the flexible nature of absolutely positioned elements. When an absolutely positioned layer is nested inside another absolutely positioned layer (in this example, the nav layer is inside the banner layer), its position isn't relative to the top and left edges of the page. Instead, a nested layer's positioning is in relation to the edges of its parent layer. In this case, the navigation layer appears 65 pixels down from the top edge of the banner no matter where the banner's placed on the page. Nested layers are discussed on Section 8.7.4.
Figure 8-19. You can use the Insert Div Tag dialog box to nest one layer inside another. 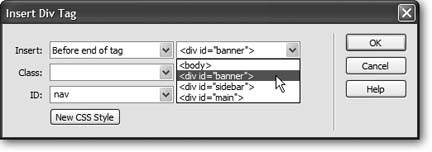 -
Click OK to insert the new layer . Dreamweaver adds a layer with the text "Content for id 'nav' Goes Here." You'll put the navigation bar here. -
Choose File  Open. Navigate to and open the file navigation.html in the DWLayout folder . Open. Navigate to and open the file navigation.html in the DWLayout folder . You can also double-click the file in the Files panel to open it. -
Select the navigation bar on the page and copy it . For example, click inside the page, choose Edit  Select All and then Edit Select All and then Edit  Copy. Copy. -
Triple-click anywhere inside the navigation layer . That is, anywhere inside the text "Content for id 'nav' Goes Here." This selects that paragraph of text. You can also click inside and choose Edit  Select All to select the contents of the <div>. Select All to select the contents of the <div>. -
Paste. The navigation bar is dumped into the layer. The page is looking great. Just one last change. The banner's too close to the top of the window. It would look better if it were just a few pixels lower. -
In the document window, move your mouse to the top edge of the banner area. When the cursor changes to a cross with four arrows, click to select the layer . Again, you can use any of the techniques listed in step 1 on Section 8.7.1. -
Press the down arrow key three times . This step moves the banner down 3 pixelsthe perfect amount. Notice that the navigation bar moves also. Because it's nested inside the banner, it always goes where the banner layer goes. -
Press F12 (Option-F12) to preview your design in a Web browser (see Figure 8-20) . Congratulations! You've had your first taste of CSS-based layout. Figure 8-20. With CSS, you can achieve most of the same layout effects available with table-based designs, using less code and with greater design flexibility.  |

 New Site
New Site 





