Hypotheses Development
|
|
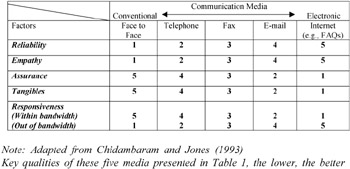
To investigate the relationship between media choice and end-user perceptions of help desk functions, a research model was developed as shown in Figure 1 and Table 1. In this model, we used five constructs from SERVQUAL (Parasuraman et al., 1991) that are thought of as being closely related to end-user satisfaction with help desks: reliability, empathy, assurance, tangibles and responsiveness.
|
|
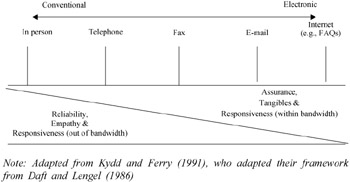
Figure 1: Continuum of Communication Media in Help Desk
We first adopted Kydd and Ferry's (1991) and Daft and Legal's (1986) continuum of communication media, and then developed a new matrix based on SERVQUAL measures. This serves as the basis for our belief that communication media differ in their relative abilities to increase reliability, empathy, assurance, tangibles and responsiveness (see Figure 1 and Table 1). As presented in Table 1, the five media, including conventional and electronic media, offer combinations with various strengths and weaknesses. On the basis of the literature, we derive the relationship between media choice and different aspects of perception of help desk function.
Conventional media provide end-users with the ability to increase reliability and empathy, because they allow end-users to exchange a variety of verbal and non-verbal information (Chidambaram & Jones, 1993). In particular, face-to-face contact has the ability to allow a broad range of communication stimuli and responses, so as to make end-users perceive a personal interest, politeness and attention, get first problem-solving cues, sincere interest and immediate answers without ambiguity. It also permits richer affection than does any form of electronic media. For example, conventional media are often considered as a more natural form of group interaction than comparable non-in person forums (Daft & Lengel, 1986). In other words, electronic media are regarded as less effective media for intense socio-emotional interaction involving heated debates, negotiation and decision-making.
On the basis of the literature reviewed above, we hypothesize that conventional media is positively associated with the perception of reliability and empathy among service quality constructs (see Figure 1). Hence:
| Ha: | The use of conventional media is more strongly related to reliability than the use of electronic media. |
| Hb: | The use of conventional media is more strongly related to empathy than the use of electronic media. |
We also hypothesize that electronic media increase assurance and tangibles. For example, written documents such as e-mail and Internet (frequently asked questions) help end-users deal with the dual themes juxtaposed by Daft and Lengel (1986). Electronic media allow end-users to focus their idea or problem (Zigurs et al., 1988) and leave evidence of communication. Thus, end-users can obtain confidence, safety, and transaction knowledge.
| Hc: | The use of electronic media is more strongly related to Assurance than the use of conventional media. |
| Hd: | The use of electronic media is more strongly related to Tangibles than the use of conventional media. |
As shown in Table 1, electronic media provide an ability to input comments anonymously and are easy for customers to access (Zigurs, Poole, & De Sanctis, 1988). These characteristics encourage end-users to easily lodge complaints, so they can receive prompt service. However, electronic media have a narrow bandwidth [1]. When electronic media deal with complex problems and out of contents, end-users are faced with more of a time lag than when they use conventional media. Thus, we assume hybrid media users (people who select mixed media determine this based on problems or their own experience) have a higher perception than conventional media users or electronic media users do.
| He: | The users of both conventional and electronic media will show a higher satisfaction on responsiveness toward help-desk services than conventional media users or electronic media users only. |
[1]According to Chidambaram and Jones (1993), they referred to bandwidth as an ability of a medium to allow a broad range of communication stimuli and responses.
|
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 186