Recipient Policies
A policy is a collection of configuration settings that can be applied across any number of objects. Changing a policy enacts the change on every object to which the policy applies. There are two types of policies in Exchange 2000 Server: system policies and recipient policies. System policies apply to server objects like databases and servers. Recipient policies apply to recipient objects like users and groups and are the focus of this discussion. Because policies can make universal changes across dozens or even hundreds of servers in your organization, they also play a large role in Exchange security.
Exchange 2000 Server includes a single built-in recipient policy used to generate e-mail addresses automatically for mail-enabled Exchange objects, such as users, groups, contacts, public folders, stores, and system attendants. You can create new policies at any time.
Recipient policies employ a "background apply" implementation to make configuration changes. You create a policy by defining the settings for that policy and associating that policy with one or more recipient objects in Active Directory. The policy is then actually applied at a later time, based on the schedule of the Address List service running under the System Attendant.
Creating a Recipient Policy
You create new recipient policies using the Exchange System snap-in. Open the Recipients folder, and then select the Recipient Policies folder inside it. Choose New Recipient Policy from the Action menu to create the new policy. This command opens the property sheet for the new policy, with the General tab showing (Figure 9-26).
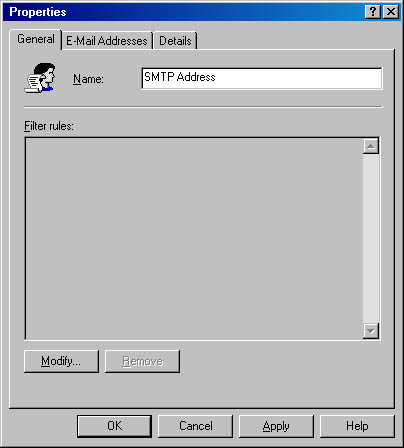
Figure 9-26. Creating a new recipient policy.
In the Name field, type a name for your recipient policy. Next click the Modify button to open a Find dialog box similar to the Find Users, Contacts, and Groups dialog box. Select the types of recipients to which you want this new policy to apply on the General tab of this dialog box, and then, on the Advanced tab, enter any custom filter settings you like, using field-level recipient attributes. Once you have defined your search criteria, click Finish to display the results in the Find window. Click OK when you finish defining your policy members. You then return to the General tab of the policy's property sheet, where you will see the filter rules you specified.
Click the E-Mail Address Policy tab (Figure 9-27). Use the options on this tab to configure rules for generating e-mail addresses for the members of the new recipient policy. The current rules are listed under Generation Rules. Make sure that the necessary addresses are selected for this set of recipients. Exchange Server uses the rules in this list to generate addresses automatically for any recipient to which this policy applies. You can create a new address generation rule by clicking the New button and choosing an address type, or you can modify an existing address generation rule by selecting the rule and clicking the Edit button. If you create a new address generation rule of the same e-mail type as an existing rule, you can make it the primary address for members of the policy.
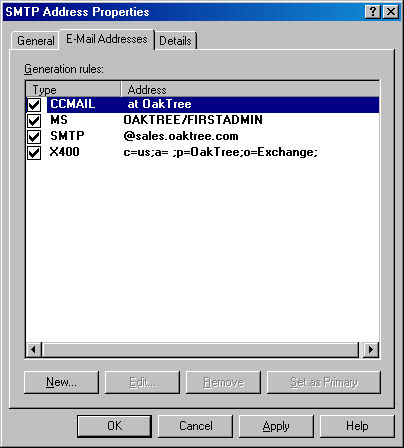
Figure 9-27. Defining rules for generating e-mail addresses.
The Recipient Updating area of the E-Mail Address Policy tab allows you to select specific tasks you want Exchange Server to perform when updating recipients. Click Set Existing E-Mail Addresses As Secondary Addresses if you want the updated address to become the primary address shown in the From field of e-mail sent by recipients to which this policy applies. Click Over-ride All Automatically Generated E-Mail Addresses if you want to replace all existing addresses created by the recipient policy. Once you have configured the new address generation policy, you can modify it at any time on this tab.
Creating an Exception to a Policy
Once you have created a policy for a group of recipients, you can override the addressing settings for individual contacts. This is known as creating an exception to the policy. You do this using the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in. Find the recipient or recipients for which you want to create an exception, and open their property sheets. Switch to the E-Mail Address Policy tab, and modify the e-mail address settings, using the same techniques you used when creating the address for the policy. This manual setting overrides any recipient policies in effect.
EAN: N/A
Pages: 193
- ERP System Acquisition: A Process Model and Results From an Austrian Survey
- The Effects of an Enterprise Resource Planning System (ERP) Implementation on Job Characteristics – A Study using the Hackman and Oldham Job Characteristics Model
- Context Management of ERP Processes in Virtual Communities
- Data Mining for Business Process Reengineering
- A Hybrid Clustering Technique to Improve Patient Data Quality