Recipe5.26.Using Mailbox Manager
Recipe 5.26. Using Mailbox ManagerProblemYou want to use the Mailbox Manager feature of Exchange Server to clean up certain items within your users' mailboxes. SolutionUsing a graphical user interface
You now need to schedule Mailbox Manager to run on each mailbox server within your organization. The same set of policies you just created will be used on each server.
Figure 5-7. Scheduling Mailbox Manager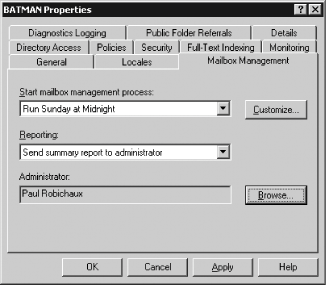 DiscussionMailbox Manager examines three MAPI properties of an object when determining whether to process an item according to the policies in place: PR_MESSAGE_DELIVERY_TIME, PR_CLIENT_SUBMIT_TIME, and PR_LAST_MODIFICATION_TIME. If all three of these properties do not meet the criteria defined within Mailbox Manager, then the object will not be removed from the mailbox. Since the PR_LAST_MODIFICATION_TIME property is reset each time a message is opened, items that you might have expected to be removed from the mailbox may still be in place. This is to ensure that objects that are currently in use within the mailbox remain active and usable. For objects such as IPM.Appointment, IPM.Task, and IPM.Journal, additional MAPI properties are checked to ensure that active and recurring appointments, active tasks, and active journaling activities are retained. You may not want mailbox manager to take action on a specific message class. In order to leave all appointment items, for instance, you can select Exclude Specific Message Classes and click Customize. You would then type IPM.Appointment in the Exclude Message Classes area and click Add. Mailbox Manager also checks for message sizes. By default, it will not remove items that are less than 1 MB. If the message size is less than 1 MB (or whatever size you modify your policy to use), it will not be deleted from the mailbox even if it is older than the age limit defined in your policy (which is 30 days in the default settings). It is always best to initially run Mailbox Manager in report mode to determine what the results of the scan will be. It's possible to create a script to duplicate the functionality of Mailbox Manager, but it seems impractical to do so, given the inherent flexibility of Mailbox Manager itself. See AlsoMS KB 302804 (Message Age Limit Properties Used by Mailbox Manager) and MS KB 319188 (How to use recipient policies to control mailboxes in Exchange 2000 and Exchange 2003) |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 235
 Recipient Policy.
Recipient Policy. Administrative Group Name
Administrative Group Name