Enterprise Administration for Farms
This section covers some of the Central Administration links that deal with administrating Search at the farm level. Within Central Administration, on the Application Management page, there is a single link, Manage Search Service, to manage farm-wide settings for Search. When you click this link, you're presented with the page shown in Figure 17-1.
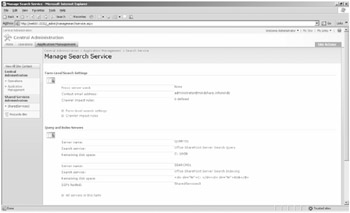
Figure 17-1: Upper portion of the Manage Search Service page
You'll note that on this page, there are three main sections:
-
Farm-Level Search Settings
-
Query And Index Servers
-
Shared Services Providers With Search Enabled (not shown in Figure 17-1)
Let's discuss each section individually.
Farm-Level Search Settings
In the Farm-Level Search Settings section, you'll see two links. The first link, Farm-Level Search Settings, takes you to the Manage Farm-Level Search Settings page. (See Figure 17-2.) On this page, you can configure four elements. First, you can configure the the Search contact e-mail address. This account should be an active account that is checked regularly and has farm-wide permissions to make configuration changes for all search settings in the farm.
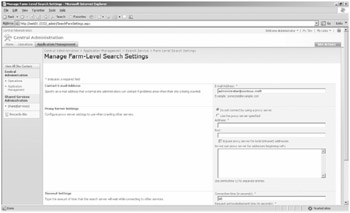
Figure 17-2: Upper portion of the Manage Farm-Level Search Settings page
The second configuration element is the proxy server settings you want search to use. Note that because this is a farm-wide setting, it will affect all SSPs in your farm and any child farms that are consuming shared services from your farm. Note also that because the Web front-end (WFE) servers actually crawl and index the content sources on behalf of the Indexing server, the WFE servers need to be on the "inside" part of your LAN and configured to connect out through your proxy server if you choose to enable proxy services.
The third configuration element of this page allows you to configure the Connection Timeout settings. The defaults are 60 seconds for both connecting to a content source and waiting for an acknowledgment from the target server. You can adjust these settings as necessary.
The fourth configuration element of this page allows you to configure the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Certificate Warning element. When this option is selected, the crawler will ignore SSL certificate warnings and continue crawling the content source over SSL. Best practice in most environments is to select this check box.
The second link in the Farm-Level Search Settings section on the Manage Search Service page is the Crawler Impact Rules link. This link will take you to the Crawler Impact Rules page. On this page, you can select to Add A New Rule, which will help configure the throttling of the crawler.
When you click the Add Rule link, you're presented with the Add Crawler Impact Rule page. (See Figure 17-3.) This page is used to throttle the crawler on a per-site (URL namespace) basis so that it doesn't overload either the content source's server, any routing hardware between the WFE servers and the target server, or bandwidth utilization.
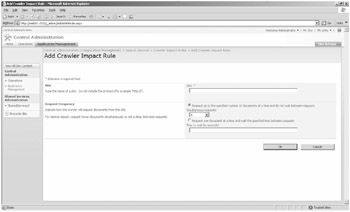
Figure 17-3: The Add Crawler Impact Rule page
Interestingly, you can enter global rules, such as *.com or *.*, or you can enter rules as specific as domain.contoso.msft. Regardless of how broad or narrow you configure your rule to be, you have one of two configuration choices for each rule. You can limit the number of documents downloaded per request (the default is eight), or you can enter a wait period between each download request (the default is zero).
| Note | If you're crawling a Web site, a document is considered to be an individual Web page regardless of the size of the page. By default, the downloads of documents occur pretty quickly, so if you really want to slow down the crawler, enter one second between requests. If you want to slow it down just a bit, scale back the number of documents that are downloaded per request. |
The configurations on the Add Crawler Impact Rule page are directly related to the Indexer Performance settings on the Configure Office SharePoint Server Search Service Settings page and override these default settings for any give site configured in the Crawler Impact Rules. To find the Configure Office SharePoint Server Search Settings page, open Central Administration, then click the Index server link in the Farm Topology Web Part. Then click the Office SharePoint Server Search Service link. Then, on the Configure Office SharePoint Server Search Service Settings page (shown in Figure 17-4), in the Indexer Performance section, you can select Reduced, Partly Reduced, or Maximum. Select the Maximum setting if you want to crawl the content as fast as you can. Select the Partly Reduced setting if you want to slow down the crawling action some but not slow it to the slowest setting, which is the Reduced setting. Despite the interface verbiage, these settings aren't so much about SQL performance and the indexing process as they are about the SQL server's performance relative to other applications that are using the same SQL server as your SharePoint farm when Maximum is selected during the crawl process. Writing metadata to the SSP's Search Database in SQL can be an intensive process if you're crawling the content source at Maximum capacity, so slowing down the crawl process means that the write actions to the SQL database (Property Store) will slow down and be less intensive, thereby improving SQL Server performance for other applications.
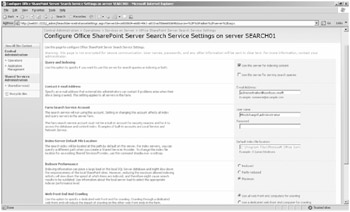
Figure 17-4: Indexer performance settings
The Indexer Performance settings are the default value for the Search settings for the farm. The crawler impact rules override these default settings. The Indexer Performance settings are tied to the number of parallel threads that the crawler uses at any given time. Based on your hardware configuration, the crawler will calculate the number of threads it will use to crawl content. The maximum number of threads that the crawler will allocate to itself is 64, though even on quad processor servers, this will not likely be needed.
If you want the crawler to use a specific number of threads during the crawl process, you can modify the RobotThreadsNumber under the HKLM\SOFTWARE \Microsoft\Office Server\12.0\Search\Global\Gathering Manager registry key. If you see a zero "0" in this value, this means that SharePoint is using the default number of threads based on your hardware configuration. If you input a value other than zero, SharePoint will use the value that you explicitly input here.
The reason you'll increase the number of crawler threads is because content sources, especially Web sites, tend to not reply instantly, so a crawling thread is likely to be blocked on the network I/O. As you increase the number of threads, up to a point, there is a higher chance that some thread will actually get a reply back and will be able to consume the CPU by filtering and indexing some document. If the crawler is utilizing the CPUs at 100 percent, this means that the content source reply rate is quick enough to have all CPUs on the server utilized by unblocked threads. When this happens, increasing the number of threads won't improve performance.
Best practice is to ensure that your CPU utilization, during a crawl process, is utilized at the maximum capacity that you decide is acceptable to you. For example, if you want the CPU(s) on your server utilized at no more than 80 percent capacity during normal crawling operations, then ensure that you set the number of crawler threads to a level where CPU utilization is sustained at 80 percent, on average.
Query and Index Servers
On the Query And Index Servers section of the Manage Search Service page, you'll find a link named All Servers In This Farm that will open the Servers In Farm page where you will find additional links that will lead you to the Configure Office SharePoint Server Search Settings page for each server in your farm that has the Search Service started.
Shared Services Providers with Search Enabled
In the Shared Services Providers With Search Enabled section of the Manage Search Service page, you can view the status of the following Search activities for each SSP in your farm:
-
Crawling status
-
Items in the index
-
Propagation status
Note that you cannot administer these parts of your Search deployment from here (you must go to the appropriate SSP for this), but you can use this as a type of information dashboard that reports on how your SSPs are functioning. For each SSP, you'll find a link to that SSP's administrative interface for convenient, fast access to managing the SSP.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 299