Foundation and Supplemental Topics
Cisco IDS ModuleThe Cisco IDS Module (IDSM) integrates Cisco IPS functionality directly into your Catalyst 6000 family switch. This line card captures traffic directly off of the switch's backplane. Beginning with Cisco IDS version 4.0, Cisco introduced the second-generation IDSM, called the IDSM-2. This new module runs the same code base as the appliance sensor. Therefore, both platforms now support the same functionality. IDSM-2 Technical SpecificationsIn deploying IDSM-2 throughout your network, it is helpful to understand its capabilities and requirements. The specifications for deploying IDSM-2 fall into the following two categories:
Performance CapabilitiesThe IDSM-2 is a single-slot switch card that provides the following enhanced capabilities:
Catalyst 6500 RequirementsUnlike the appliance sensor, the IDSM-2 is a switch card. Therefore, to deploy the IDSM-2 you must have a Catalyst 6500 family switch. Furthermore, to successfully use your IDSM-2 as another component in your overall Cisco IPS solution, your switch operating system must fulfill one of the following requirements:
If you have Catalyst OS 7.5(1) or later, you also need to have one of the following supervisor engines:
If you have IOS Release 12.1(19)E or later, you also need to have one of the following supervisor engines:
Note Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(14)SY requires Supervisor Engine 2 and MSFC2, and Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(14)SX1 requires Supervisor Engine 720. Although meeting the operating system version on your supervisor engine enables you to install and use the IDSM-2 on your switch, there are a few other requirements, depending on the features that you plan to use in conjunction with the IDSM-2. You have several traffic-capture options on your Catalyst switch. The most common is probably the Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) feature. If you plan to capture traffic using VLAN Access Control Lists (VACLs), however, you also need to have a Policy Feature Card (PFC). Your IDSM-2 also supports device management. This means that it can dynamically restrict network traffic by updating access controls on various network devices, such as the following:
Key FeaturesOriginally, the IDSM incorporated IDS functionality directly into your switch infrastructure. This original switch sensor included the following functionalities:
This first-generation switch sensor, however, did not provide all of the functionality of the appliance sensors. To enhance the capability of the switch sensor, the IDSM-2 provides more capabilities than the original IDSM. Besides increasing the bandwidth capacity of the IDSM-2, it provides the following capabilities or features:
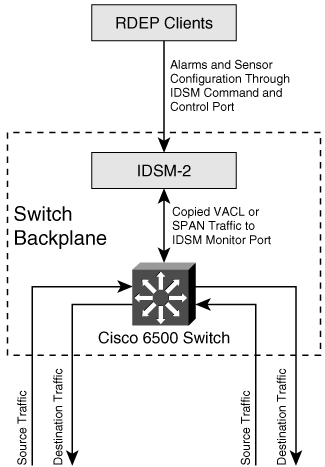
IDSM-2 Traffic FlowUnlike traffic flow to the network appliance, the traffic flow to the IDSM-2 line card requires a little more explanation (see Figure 13-1). Furthermore, understanding this traffic flow is an important aspect of effectively using your IDSM-2 to capture and analyze network traffic. Although the IDSM-2 receives traffic directly from your switch's backplane, your Catalyst 6500 family switch must be configured to enable traffic to flow to and from the various ports on the IDSM-2 line card. Figure 13-1. IDSM-2 Traffic Flow Traffic that enters the Catalyst 6500 switch is destined for a host or network. After passing through the switch, a copy of this traffic is diverted through the switch backplane to your IDSM-2 for intrusion-detection analysis. As in the appliance sensors, alerts are stored in the Event Store until your monitoring application retrieves these alarms via the command and control interface by using the Remote Data Exchange Protocol (RDEP). IDSM-2 ConfigurationSince the IDSM-2 has the same code base as the appliance sensor, the initialization steps performed on the appliance sensor also apply to the IDSM-2. The major difference between the appliance sensor and the IDSM-2 is that you need to configure the capture ports on the IDSM-2, and you need to initially access the command-line interface (CLI) through the switch. The IDSM-2 capture ports are internally connected to the switch's backplane; this structure differs from that of the appliance sensor, where you physically connect the monitoring ports to your switch (or other network device) via Ethernet cables. To enable your IDSM-2 to become a functional component of your Cisco IPS, perform the following basic initialization tasks:
Verifying IDSM-2 StatusAfter installing the IDSM-2 on your Catalyst 6500 family switch, you can verify that the switch has recognized the IDSM-2 line card via the show module switch command (see "Catalyst 6500 Commands" later in this chapter). Executing this command provides detailed information about the line cards in your switch. You should see a line similar to the following for your IDSM-2 line card (if using CatOS): 8 8 8 Intrusion Detection Syste WS-SVC-IDSM2 yes ok The "ok" indicates that the card is working, and the correct name indicates that the switch correctly recognizes the line card. The similar line for IOS looks like the following: Mod Ports Card Type Model Serial No. --- ----- -------------------------------------- ------------------ ----------- 9 2 Intrusion Detection System WS-X6381-IDS SAD05050GDY Mod MAC addresses Hw Fw Sw Status --- ---------------------------------- ------ ------------ ------------ ------- 9 0003.3282.ee0a to 0003.3282.ee0b 1.1 4B4LZ0XA 3.0(5)S23 Ok Note It is normal for the show module command to display a status of "other" instead of "ok" when IDSM is first installed. When the IDSM-2 completes its diagnostic routines and comes online, the status will change to "ok," but this can take up to 5 minutes. Initializing the IDSM-2The basic initialization tasks for the IDSM-2 are the same as for the appliance sensor. (See Chapter 2, "IPS Command-Line Interface.") These tasks include the following:
Other tasks that you might need to perform during initialization include the following:
One of the benefits of having the same code base on both the appliance sensor and the IDSM-2 is that the configuration tasks are very similar, which reduces the total amount of knowledge needed to install both types of sensors. Although the sensor appliance can be configured to use either its internal clock or Network Time Protocol (NTP), the IDSM-2 can only be configured to use either the switch's time or NTP. The IDSM-2 cannot be configured to use an internal clock. Therefore, there is no option to set the clock time in the IDSM-2 CLI. By default, the IDSM-2 is configured to use the switch's time. The switch converts its local time into the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) that is used by the sensor to time-stamp its events. Because the sensor's time zone is also configurable, the sensor uses its time zone and summer time settings to convert the UTC to local time. The sensor uses both its local time and UTC time settings for time- stamping events, as well as for other time functions. For this reason, it is important to ensure that the time zone and summer time settings are correct on both the switch and the IDSM-2, and to set the clock on the switch to the correct time. Note The switch only sends a UTC time to the IDSM-2. Therefore, the IDSM-2 can not convert the time using the switch's time zone and summer time settings, because these settings are not reported to the module. Accessing the IDSM-2 CLIYou initially access the IDSM-2 from the switch console. When using CatOS, the session switch command gives you access to the IDSM-2 CLI. The syntax for the Catalyst operating system session command is as follows: session mod The term mod indicates the slot where the IDSM-2 is located. When using IOS, you access the IDSM-2 CLI by using the session slot switch command. The syntax for the IOS session slot command is as follows: session slot mod {processor processor-id} Suppose that your IDSM-2 is in slot 5. The IOS command to access the IDSM-2 CLI would be as follows: Switch# session slot 5 processor 1 Note Currently, the only processor ID supported by the IDSM-2 is 1. Logging in to the IDSM-2As with the appliance sensors, you initially log in to the IDSM-2 with a username and password of "cisco." After logging in, you must immediately change the password to this account for security reasons. Configuring the Command and Control PortTo enable your monitoring applications and management software (such as IDM and Security Monitor) to communicate with your IDSM-2, you need to configure the command and control port on the IDSM-2. This includes assigning the command and control port an IP address, configuring the default gateway for the IDSM-2 command and control port, and assigning the command and control port to the correct management VLAN. Configuring the Switch Traffic Capture SettingsBesides establishing management access, you need to configure the capture ports on your IDSM-2 so that your switch sensor can analyze your network traffic. Capturing important network traffic (while not exceeding the IDSM-2's 600-Mbps capacity) is the key to successfully deploying the IDSM-2 on your network. IDSM-2 PortsTo perform its operation, the IDSM-2 uses four internal ports that fall into the following three functional categories:
Note The ports on the IDSM-2 are not physical ports that you can see. Instead, they are directly connected into the switch's backplane. TCP Reset PortThe initial version of IDSM did not provide the capability to initiate TCP resets in response to attack traffic. This limitation has been overcome in IDSM-2 by the inclusion of a port specifically for generating TCP resets. A TCP reset port was necessary because the two monitoring ports on the IDSM-2 cannot transmit the TCP reset packets. Plus this enables the monitoring ports to focus strictly on capturing traffic. Port 1 on the IDSM-2 is used for TCP reset traffic. You need to configure port 1 with the same settings (with respect to VLANs) as your promiscuous monitoring ports. It will not be monitoring any traffic, but it needs to be able to generate a TCP reset for any connection that your IDSM-2 promiscuous monitoring ports can analyze. Command and Control PortYour management application needs to be able to communicate with the IDSM-2 to change its configuration and operating characteristics. Your monitoring application needs to access the IDSM-2 to retrieve alerts. Both of these operations are conducted through the command and control interface. Port 2 on the IDSM-2 is the command and control interface. You will configure an actual IP address for this port (and assign the appropriate VLAN on your switch) to make your IDSM-2 accessible from the network. Monitoring PortsThe last two ports on the IDSM-2 are the monitoring ports. Your IDSM-2 receives all of the network traffic that it analyzes through these two monitoring ports. Ports 7 and 8 are the monitoring ports on the IDSM-2. You can use either or both of these ports to monitor your network traffic. Because of processor limitations, the IDSM-2 is capable of processing only 600 Mbps of network traffic. The two monitoring interfaces are easily capable of exceeding the 600-Mbps limitation, so you must be careful to not overload your IDSM-2 with too much traffic. Note The reason that the IDSM-2 has two monitoring ports is that it uses the same accelerator card that is used by the IDS-4250 appliance sensor. Catalyst 6500 Switch ConfigurationA significant portion of the initial setup of your IDSM-2 involves configuring the switch to send traffic to your IDSM-2 monitoring ports and enabling external applications to access the IDSM-2 via the command and control port. Configuring the Command and Control PortYour management and monitoring applications (such as IDM and Security Monitor) access the IDSM-2 through the command and control interface. When initially configuring the IDSM-2 through its CLI, you assign the command and control interface an IP address and default gateway. To complete the configuration of the command and control port, however, you must also assign the correct VLAN to the command and control port on the Catalyst 6500 switch. Setting VLANs by Using IOSIf your switch is running IOS, you can assign a VLAN to the command and control port by using the switchport access vlan interface configuration command. Setting VLANs by Using CatOSTo define a VLAN for a port on your Catalyst 6500 switch (running CatOS), use the set vlan command. This command groups one or more switch ports into a single VLAN. You can also use this command to set the private VLAN type or unmap VLANs. These extra features are explained in the Catalyst switch documentation. The syntax for the basic set vlan command is as follows: set vlan vlan_num mod/ports The parameters for the set vlan command are explained in Table 13-2.
Note The IDSM-2 command and control port (port 2) must be assigned to a VLAN that can communicate with your management and monitoring applications. Otherwise, you will not be able to configure the IDSM-2 or retrieve alarm information. To assign ports 4 through 8 on module 3 to VLAN 120 (using CatOS), use the following command: Console> (enable) set vlan 120 3/4-8 VLAN 120 modified. VLAN Mod/Ports ---- ----------------- 120 3/4-8 Console> (enable) Note If your switch is running IOS, you can assign a VLAN to the command and control port by using the switchport access vlan interface configuration command. Monitored TrafficThe IDSM-2 has the processing power to capture and analyze approximately 600 Mbps of network traffic. This traffic is captured directly off of the switch's backplane. To analyze traffic, your IDSM-2 must receive traffic on its monitoring ports (port 7 and port 8). You need to configure your Catalyst switch to copy selected traffic to the monitoring ports on your IDSM-2 line card. You can use the following three mechanisms to capture your network traffic:
Each of these options is explained in detail in Chapter 15, "Capturing Network Traffic." IDSM-2 Administrative TasksWhen using your IDSM-2, besides configuring the normal operational characteristics, you may also need to perform the following two administrative tasks:
Enabling Full Memory TestBy default, the IDSM-2 performs a partial memory test when it boots. In some troubleshooting situations, you may need to run a complete memory test. If your switch is running CatOS, you can configure your IDSM-2 to run a complete memory test by using the set boot device switch command. (Refer to the Cisco documentation for detailed information on this command.) Caution A full memory test will take significantly more time (up to 12 minutes) than a partial memory test. This will considerably increase the time that it takes your IDSM-2 to come online. Stopping the IDS ModuleTo prevent corruption of the IDSM-2, you must shut it down properly. To properly shut down the IDSM-2, you need to log in to the IDSM-2 and execute the reset command. The reset command on the IDSM-2 CLI enables you to reboot and power down the IDSM-2. The syntax for this command is as follows: reset [powerdown] The reset command without any options will cause the IDSM-2 to perform an orderly reboot. If you add the powerdown option, the IDSM-2 will perform an orderly shutdown and will either power off the device or place it in a state where it can be powered off. Note Do not remove the IDSM-2 line card from the switch until the module has shut down completely. Removing the module without going through the shutdown procedure can damage the module. Troubleshooting the IDSM-2You may need to troubleshoot the operation of your IDSM-2. Besides running various commands on your Catalyst 6500 switch, you can examine the status LED on the IDSM-2 itself. IDSM-2 Status LEDThe front panel of the IDSM-2 contains a single LED. This LED provides you with a visual indication of the state of the IDSM-2 line card. This LED can be in one of the states listed in Table 13-3.
Catalyst 6500 CommandsSince the IDSM-2 is a line card in your Catalyst switch, you can use several switch commands to examine its operation. The following three commands provide detailed information on your IDSM-2 line card and its ports:
show module CommandThe show module CatOS switch command enables you to display information about the line cards that you have installed in your Catalyst 6500 switch. The syntax for the show module command is as follows: show module [mod] The only parameter, mod, indicates the module number that the card is in. For instance, on a 6509 you have nine slots, so the module numbers are numbered from one to nine. If your IDSM-2 line card is in slot 8, you could view its information with the show module command in Example 13-1. Example 13-1. Viewing the Status of the IDSM-2 Module in Slot 8Cat6k> show module 8 Mod Slot Ports Module-Type Model Sub Status --- ---- ----- ------------------------- ------------------- --- -------- 8 8 8 Intrusion Detection Syste WS-SVC-IDSM2 yes ok Mod Module-Name Serial-Num --- -------------------- ----------- 8 SAD062004LV Mod MAC-Address(es) Hw Fw Sw --- -------------------------------------- ------ ---------- ----------------- 8 00-e0-b0-ff-3b-80 to 00-e0-b0-ff-3b-87 0.102 7.2(0.67) 4.1(0.3)S42(0.3 Mod Sub-Type Sub-Model Sub-Serial Sub-Hw Sub-Sw --- ----------------------- ------------------- ----------- ------ ------ 8 IDS 2 accelerator board WS-SVC-IDSUPG . 2.0 Cat6k> You can also specify the show module CatOS command without any parameters to obtain some basic information about all the line cards in your switch, as displayed in Example 13-2. Example 13-2. Viewing the Status for All of the Modules in a Catalyst 6500 SwitchCat6k> show module Mod Slot Ports Module-Type Model Sub Status --- ---- ----- ------------------------- ------------------- --- -------- 1 1 2 1000BaseX Supervisor WS-X6K-SUP1A-2GE yes ok 15 1 1 Multilayer Switch Feature WS-F6K-MSFC no ok 3 3 48 10/100BaseTX Ethernet WS-X6548-RJ-45 no ok 4 4 8 1000BaseX Ethernet WS-X6408-GBIC no ok 6 6 8 Intrusion Detection Syste WS-SVC-IDSM2 yes ok 8 8 8 Intrusion Detection Syste WS-SVC-IDSM2 yes ok 9 9 16 10/100/1000BaseT Ethernet WS-X6516-GE-TX no ok Mod Module-Name Serial-Num --- -------------------- ----------- 1 SAD04200CUH 15 SAD04190BS5 3 SAD0612021X 4 JAB04040859 6 SAD0625018D 8 SAD062004LV 9 SAL06365QSP Mod MAC-Address(es) Hw Fw Sw --- -------------------------------------- ------ ---------- ----------------- 1 00-30-7b-95-26-86 to 00-30-7b-95-26-87 3.2 5.3(1) 7.6(1) 00-30-7b-95-26-84 to 00-30-7b-95-26-85 00-09-44-89-90-00 to 00-09-44-89-93-ff 15 00-30-7b-95-00-3c to 00-30-7b-95-00-7b 1.4 12.1(13)E3 12.1(13)E3 3 00-01-63-d7-5a-ca to 00-01-63-d7-5a-f9 4.2 6.3(1) 7.6(1) 4 00-30-a3-38-9a-30 to 00-30-a3-38-9a-37 2.3 4.2(0.24)V 7.6(1) 6 00-10-7b-00-0e-e8 to 00-10-7b-00-0e-ef 0.102 7.2(1) 4.1(0.3)S42(0.3 8 00-e0-b0-ff-3b-80 to 00-e0-b0-ff-3b-87 0.102 7.2(0.67) 4.1(0.3)S42(0.3 9 00-09-11-e4-89-c4 to 00-09-11-e4-89-d3 2.2 6.3(1) 7.6(1) Mod Sub-Type Sub-Model Sub-Serial Sub-Hw Sub-Sw --- ----------------------- ------------------- ----------- ------ ------ 1 L3 Switching Engine WS-F6K-PFC SAD04200DP9 1.1 6 IDS 2 accelerator board WS-SVC-IDSUPG . 2.0 8 IDS 2 accelerator board WS-SVC-IDSUPG . 2.0 Cat6k> IOS also provides a show module command to display the status of the line cards. This output is similar to the CatOS output but is slightly different. Specifying the show module IOS command without any parameters generates output similar to that in Example 13-3. Example 13-3. Showing Module Status When Running IOSCat6500#show module Mod Ports Card Type Model Serial No. --- ----- -------------------------------------- ------------------ ----------- 1 2 Catalyst 6000 supervisor 2 (Active) WS-X6K-SUP2-2GE SAL0605HFH7 2 48 48 port 10/100 mb RJ-45 ethernet WS-X6248-RJ-45 SAD050504C1 4 48 48 port 10/100 mb RJ45 WS-X6348-RJ-45 SAD041606Y5 5 6 Firewall Module WS-SVC-FWM-1 SAD060300N9 6 6 Firewall Module WS-SVC-FWM-1 SAD0707016K 8 2 Intrusion Detection System WS-X6381-IDS SAD03403897 9 2 Intrusion Detection System WS-X6381-IDS SAD05050GDY Mod MAC addresses Hw Fw Sw Status --- ---------------------------------- ------ ------------ ------------ ------- 1 0006.d65a.9694 to 0006.d65a.9695 3.5 6.1(3) 7.5(0.6)HUB2 Ok 2 0001.c96d.64d0 to 0001.c96d.64ff 1.4 5.4(2) 7.5(0.6)HUB2 Ok 4 00d0.c0cd.86c8 to 00d0.c0cd.86f7 1.1 5.3(1) 7.5(0.6)HUB2 Ok 5 00e0.b0ff.3438 to 00e0.b0ff.343f 0.201 7.2(1) 2.3(0)60 Ok 6 0002.7ee4.f610 to 0002.7ee4.f617 1.1 7.2(1) 2.3(0)60 Ok 8 00e0.140e.f7ec to 00e0.140e.f7ed 0.201 4B4LZ0XA 7.5(0.6)HUB2 PwrDown 9 0003.3282.ee0a to 0003.3282.ee0b 1.1 4B4LZ0XA 3.0(5)S23 Ok Mod Sub-Module Model Serial Hw Status --- --------------------------- --------------- --------------- ------- ------- 1 Policy Feature Card 2 WS-F6K-PFC2 SAL06100RH2 3.2 Ok 1 Cat6k MSFC 2 daughterboard WS-F6K-MSFC2 SAL06090F5F 2.2 Ok 4 Inline Power Module WS-F6K-PWR 1.0 Ok Mod Online Diag Status --- ------------------- 1 Pass 2 Pass 4 Pass 5 Pass 6 Pass 8 Unknown 9 Not Supported Cat6500# show port CommandYou can use the show port (CatOS) command to examine the different ports on your switch. While debugging, you might want to see the packet statistics and error information for the monitoring ports on your IDSM-2. If your IDSM-2 line card is in slot 8, you can examine the first monitoring port with the show port command in Example 13-4. Example 13-4. Showing Port Status When Running CatOSCat6k> show port 8/7 * = Configured MAC Address Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type ----- -------------------- ---------- ---------- ------ ----- ------------ 8/7 connected trunk full 1000 Intrusion De Port Broadcast-Limit Multicast Unicast Total-Drop Action -------- --------------- --------- ------- -------------------- ------------ 8/7 - - - 0 drop-packets Port Status ErrDisable Reason Port ErrDisableTimeout Action on Timeout ---- ---------- ------------------- ---------------------- ----------------- 8/7 connected - Enable No Change Port Align-Err FCS-Err Xmit-Err Rcv-Err UnderSize ----- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- --------- 8/7 0 0 0 0 0 Port Single-Col Multi-Coll Late-Coll Excess-Col Carri-Sen Runts Giants ----- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- --------- --------- --------- 8/7 0 0 0 0 0 0 - Port Last-Time-Cleared ----- -------------------------- 8/7 Fri May 16 2003, 16:50:42 Idle Detection -------------- -- Cat6k> show trunk CommandThe VLANs that the monitoring ports on your IDSM-2 are trunking determine what traffic is actually received by your IDSM-2. Initially, the monitoring ports are configured to trunk all of the VLANs on your switch, but you may need to change this configuration to support multiple IDSM-2 line cards and limit broadcast traffic to the IDSM-2. To examine which trunks a specific port is trunking, use the show trunk (CatOS) switch command. If your IDSM-2 line card is in slot 8, you can examine the trunks supported by the second monitoring port with the show trunk command, as in Example 13-5. Example 13-5. Showing Trunk Port Status When Running CatOScat6k> (enable) show trunk 8/8 * - indicates vtp domain mismatch Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan -------- ----------- ------------- ------------ ----------- 8/8 auto negotiate not-trunking 140 Port Vlans allowed on trunk -------- --------------------------------------------------------------------- 8/8 1-1005,1025-4094 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain -------- --------------------------------------------------------------------- 8/8 140 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned -------- --------------------------------------------------------------------- 8/8 cat6k> (enable) |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 119