Choosing PC Cards
The purpose of the PC card is to enhance the capabilities of a computer. Adding a card to your computer enables you to customize it for your needs. Without this feature, the computer would not be as modular and would not allow you to add devices chosen to meet your specific needs.
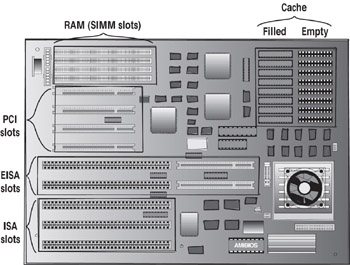
Several types of PC cards exist, such as those providing sound, network, video, and input/output capabilities. Regardless of the type of PC card, they attach to the computer by plugging into an available expansion bus slot on the motherboard. The expansion bus provides a pathway that links the device with the CPU and memory inside the computer.
There are several expansion bus design standards. It is important that you identify the slot type before purchasing a new PC card. Each bus design standard has a primary connector and might have one or more extension connectors to allow for additional capabilities. Other differences include the operating speed, interface, and method of configuration.
Bus Standards
When you are selecting a computer to purchase or build, you want to make sure that you are investing in the best technology to meet your needs. Most computers today will include support for the older ISA standard as well as support for the modern PCI standard. It is important to select a computer that includes enough slots for your expansion cards. This table defines the key differences between the standards.
| Bus Type | Interface | Speed | Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISA | 8-bit or 16-bit | 8-10MHz | Hardware or software |
| MicroChannel | 16-bit or 32-bit | 10-20MHz | Hardware or software |
| EISA | 32-bit | 8-10MHz | Software |
| VL-Bus | 32-bit | 40MHz | Hardware |
| PCI | 32-bit or 64-bit | 33MHz | Plug and Play |
| PCMCIA | 16-bit | 33MHz | Software |
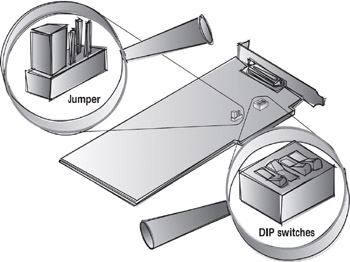
Unlike DIP switches, jumpers are still found on motherboards, hard drives, CD-ROMs, and some adapter cards. Jumpers are small connectors that are used to connect two pins to make a complete circuit. For example, most motherboards have a password jumper. The password jumper can be used to erase a system password used when the computer first boots up. Most systems require that you remove the jumper for a set period of time to erase the password.
Plug and Play
Plug and Play technology was added to Windows 95 as a way to greatly simplify the installation and configuration of new hardware. Microsoft Plug and Play is currently supported with Windows 9x, Windows Me, Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 operating systems. Plug and Play works quite well now that most hardware manufacturers design and build their hardware to be Plug and Play compatible.
The technology works something like this: New hardware is installed into a Windows XP computer. When the computer is first turned on, the BIOS checks to see what devices are attached to the motherboard or to any of the external ports. If it detects a new device, it notifies the operating system. After Windows XP starts up, the Plug and Play Wizard loads. If the new device is recognizable by Windows XP, the software is automatically loaded from the hard drive. Also, the software is automatically configured by Windows XP. Only in rare cases does Windows XP need assistance to configure a Plug and Play device. If the new device does not have software loaded into Windows XP, you will be presented with an option to insert media that contains the necessary software.
Most adapter cards in the last couple of years have been designed to the Plug and Play specification. Older cards that are not Plug and Play compatible require manual configuration through hardware, which consists of setting jumpers and dual in-line package (DIP) switches. This method of hardware configuration is nearly obsolete in most new hardware.
| Note | Although Windows NT 4 does not support Plug and Play capability, it is a feature of Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003. But Plug and Play works only for devices that are included in Microsoft's Hardware Compatibility List (HCL). Devices on the HCL have been tested and verified to be compatible with Windows. If the device you are considering for use is not included on the HCL, you should seriously consider using another device that is compatible. Besides the possibility of the device not working or causing Windows errors, Microsoft may not support your installation. You should also note that some motherboards require you to enable Plug and Play support through the computer's BIOS. |
Unlike DIP switches, jumpers are still found on motherboards, hard drives, CD-ROMs, and some adapter cards. Jumpers are small connectors that are used to connect two pins to make a complete circuit. For example, most motherboards have a password jumper. The password jumper can be used to erase a system password used when the computer first boots up. Most systems require that you remove the jumper for a set period of time to erase the password.
|
|
- Chapter VIII Personalization Systems and Their Deployment as Web Site Interface Design Decisions
- Chapter X Converting Browsers to Buyers: Key Considerations in Designing Business-to-Consumer Web Sites
- Chapter XI User Satisfaction with Web Portals: An Empirical Study
- Chapter XIII Shopping Agent Web Sites: A Comparative Shopping Environment
- Chapter XV Customer Trust in Online Commerce