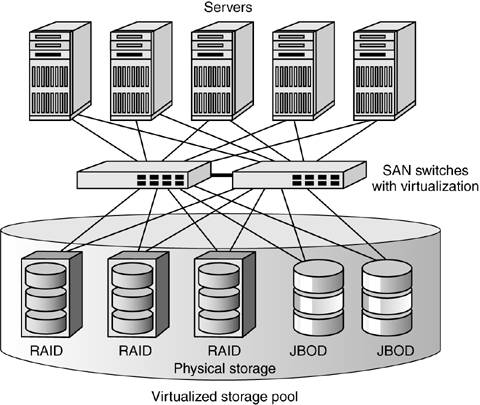
11.4 SAN Interconnect-Based Storage Virtualization
| Interconnect-based virtualization solutions move the virtualization intelligence into the heart of the SAN, either as a third-party appliance or as enhanced functionality within a Fibre Channel or Gigabit Ethernet SAN switch. The rationale behind interconnection-based virtualization is that because the storage network already provides connectivity between all servers and storage devices, it can more easily intercept and process storage requests transparently. No special agents are required on the host systems, and any mix of storage targets can be supported. All that is required is sufficient processing power on the appliance or SAN switch to manipulate metadata and still provide wire-speed data transport. As shown in Figure 11-7, in an interconnection-based virtualization solution, servers may attach to SAN switches as usual, with dual pathing for failover or load balancing. Unlike traditional SAN attachment, however, the servers do not discover individual physical storage devices on the SAN. Instead, the virtualization intelligence in the SAN interconnection (in this example, in the SAN switches themselves) presents a logical view of a storage pool. Individual servers are assigned LUNs within the pool but are not aware of which storage devices are actually supporting the data blocks those LUNs represent. For high availability, the interconnection-based virtualization engines may provide mirroring between, for example, a RAID array and a JBOD. This is transparent to the server, which nonetheless benefits from the mirroring done on its behalf. Figure 11-7. Network-based virtualization in a redundant SAN switch configuration
In this illustration, the switch-based virtualization is deployed in a redundant configuration, ensuring dual paths to both servers and storage as well as redundancy for the virtualization engines. For this to work, the virtualization engines must be constantly synchronized to ensure that each has a duplicate and current image of the metadata of the other. As with server clustering, a heartbeat protocol keeps both engines aligned and triggers failover if a switch or virtualization entity within it fails. Interconnect-based storage virtualization offers significant advantages and disadvantages. In its support, network-based virtualization is completely transparent to servers, and so it readily accommodates heterogeneous server environments and minimizes server administrative tasks. It is also completely transparent to the storage targets, enabling any mix of enterprise-class or departmental RAID or JBODs from any vendor. As an in-band solution, however, interconnect-based virtualization does pose a potential bottleneck in terms of performance. Vendors must demonstrate that their interconnect-based appliances can provide all the benefits of virtualization without imposing a performance penalty. The main drawback of switched-based virtualization in particular is that it places an enormous responsibility on products that were originally designed for relatively simple switching tasks. Even at additional cost, providing a product that combines high-performance SAN switching with complex virtualization management is not a trivial task. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 171