What Is Bluetooth?
Bluetooth is the transmitting hardware operating within the frequency range from 2.400 to 2.4835 MHz (not just 2.4 MHz, as most users think). Microwave ovens, wireless networks corresponding to the 802.11b/g standard, radiotelephones, and many other devices operate in the same frequency range; therefore, all these devices conflict aggressively. To solve this problem, Bluetooth technology uses a special algorithm of frequency hopping . The entire frequency range is divided into 79 channels, the width of each channel being 1 MHz. Every 625 ¼ s (1600 times per second) Bluetooth devices change the channel, choosing channels according to a pseudorandom principle. Each period is called a time slot, or simply a slot. The data being transmitted are divided into packets, 2,745 bits each, and each packet is "spread" over several time slots (five time slots total).
The devices communicate according to the master ”slave relationship. Each master can have up to seven slaves. The master broadcasts in slots with even numbers, and the slave respond in slots with odd numbers .
Two types of communication are supported: Asynchronous ConnectionLess (ACL) and Synchronous Connection Oriented (SCO). The synchronous operating mode is mainly used for voice transmission, and the asynchronous mode is intended for data exchange.
The theoretical bandwidth of a channel operating in asynchronous mode is 1 Mbps, and 20% of the bandwidth is required for headers and other auxiliary information. Thus, only about 820 Kbps are available for user data. In practice, however, this value depends on the communications quality and on the specific features of the design typical for a given transmitter. Master and slave devices can have only one link for asynchronous communications, organized according to the point-to-point design or operating in the broadcast mode. The slave cannot switch to the asynchronous transmission mode.
In synchronous mode, the master can support up to three channels to one, two, or three slave devices. In this case, the bandwidth of each channel is 64 Kbps. Transmission is carried out in slots assigned by the master. Slots that are not used in synchronous mode can be used for asynchronous transmission. The general Bluetooth transmission protocol is shown in Fig. 29.2.
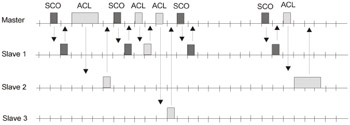
Figure 29.2: Operating method of the Bluetooth transmission protocol
According to the specifications, the maximum allowed power of the transmitter must be 10 mW, which ensures stable operation within a radius of 10 to 25 meters .
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 164