Understanding Directories
Looking at the contents of the File Manager can be a bit daunting. There are so many different directories, most with three-and four-letter names , that seem to make no sense. There is actually a lot of sense in what seems to be file madness. Although there is no standard for Linux directories, some common directories have emerged. There are basically three different categories of directories in Lindows. There is the master directory, which contains all the files and directories on your computer, there are administrative directories used for system functions, and there are user directories, which each user can access.
The Master Directory
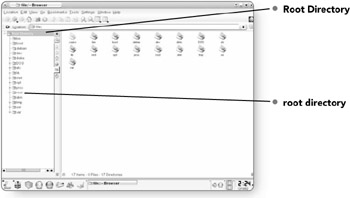
When you open the File Manager, you'll notice that all the directories on your computer fall within the master directory, which is called the Root directory. The master directory is also known as the slash directory because if you put a forward slash (/) in the Location field of the File Manager, you will see all the contents of the Root directory.
| Note | To make things more confusing there are actually two root directories in Lindows. There is the master directory called the Root directory, but there is also a directory within the master directory called root. |
-
Root Directory . This is the master directory that contains all the files on your machine. It is also called the slash directory because it can be accessed by putting a slash in the Location field.
-
root directory . Not to be confused with the master directory, this is a separate directory for the files of the administrator of the computer.
Administrative Directories
Administrative directories make up most of the directories on your Lindows machine, and they include everything to do with the operation of the computer, including system files, programs, and device files.
-
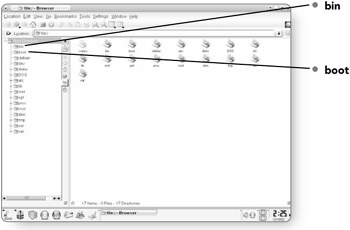
bin . Bin actually stands for "binaries." This directory contains most of the basic UNIX commands for your computer.
-
boot . This directory contains the files necessary for starting the operating system. It contains the kernel image (the kernel is the core of the operating system), that allows your software to communicate with your hardware.
-
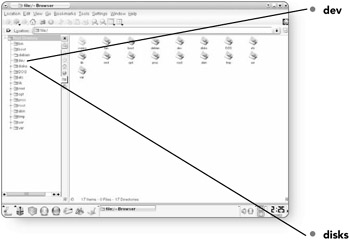
dev . Dev stands for "devices." This directory contains files that control the many devices and ports found on your system.
Note Do not manipulate files in the dev directory unless you know exactly what you are doing, as you can cause devices on your machine to malfunction.
-
disks . If you have more than one hard disk or partition, this folder will hold the related files.
-
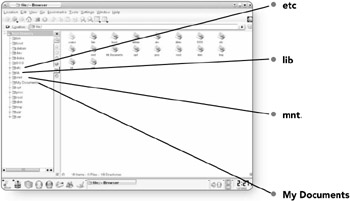
etc . Etc holds configuration files for those programs that need to be configured for the entire system.
-
lib . This directory contains libraries, which are a collection of functions that a program uses.
-
mnt . This directory contains files for specific devices that have been installed on your computer, like a CD-ROM, a floppy drive, or any other storage device.
-
My Documents . This folder is just a shortcut to the My Documents folder in the Root directory. It was created in the master directory to give you quick access to your files.
-
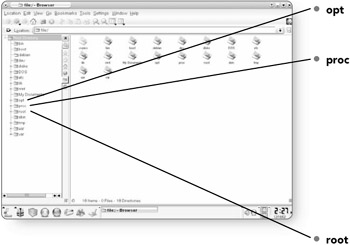
opt . Opt contains files and directories for add-on applications.
-
proc . The proc directory contains folders that are stored in the computer's memory. It contains specific information about what is currently going on in the computer. Proc is called a "pseudo file" because the files contained within aren't really there, they are just a part of the computer's memory.
-
root . This contains the files of the administrator or super user of the computer. It contains all the program's settings. If you come from a Windows environment, root is the equivalent to the My Documents folder.
-
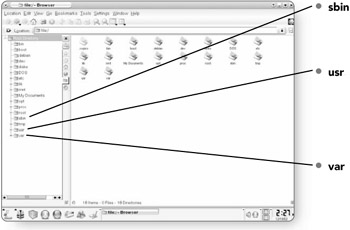
sbin . Sbin contains binary files used for system administration. Functions like poweroff are stored here.
-
usr . The directories within the usr directory contain all the software and libraries on your system. When you install a program, the application files are found in this directory.
-
var . This directory stores files that vary in size as the computer is running. Spool files and system logs are found in this directory.
User Directories
Because Lindows allows you to have multiple users for one machine, there are special user directories that each user sees when looking at their files in the File Manager.
-
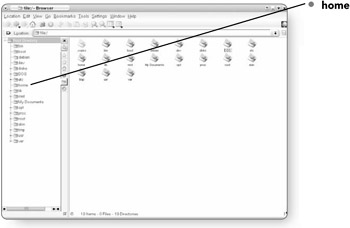
home . Home includes all of the directories for multiple users.
Note Although individual users can restrict access to their home folder so no other user can access it, the root user (or administrator) always has access to everyone's folder, regardless of the permissions set.
-
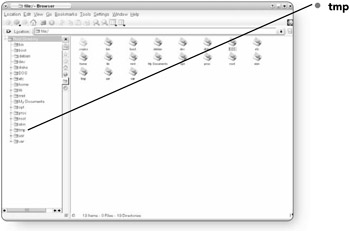
tmp . Tmp stands for temporary files. Files that the system temporarily creates are stored in this folder.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 152