The nodeName Property
The nodeName PropertyThe nodeName property gives you the name of a node, and it's a property you use when you're treating an HTML document as a W3C DOM node tree. You can see the support for this property in Table 5.36. Table 5.36. The nodeName Property
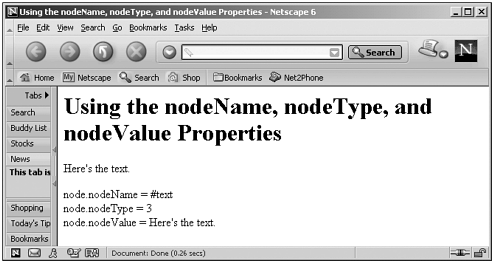
The nodeName of an element is the element's name (just like the tagName property). The nodeName of an attribute is the name of the attribute. The nodeName for a text node is "#text" , because text nodes don't have specific names . Here's an example that puts the nodeName , nodeType , and nodeValue properties to work. In this case, I'll take a look at those properties for a text node: (Listing 05-17.html on the web site)<HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE> Using the nodeName, nodeType, and nodeValue Properties </TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY> <H1>Using the nodeName, nodeType, and nodeValue Properties</H1> <P NAME="text1" ID="text1"> Here's the text. </P> <SCRIPT LANGUAGE="JavaScript"> <!-- var node = document.getElementById("text1").firstChild document.write("node.nodeName = " + node.nodeName + "<BR>") document.write("node.nodeType = " + node.nodeType + "<BR>") document.write("node.nodeValue = " + node.nodeValue + "<BR>") // --> </SCRIPT> </BODY> </HTML> You can see the results in Figure 5.13, where the nodeName , nodeType , and nodeValue properties for the text node are displayed. Figure 5.13. Using the nodeName , nodeType , and nodeValue properties. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||