Implementing RSA Public Key Encryption
The RSA encryption has been described in earlier chapters. This chapter shows an implementation of the RSA algorithm. There are really two parts in developing a cipher Service Provider Interface (SPI): understanding how to implement the SPI layer with the javax.crypto.CipherSpi class and understanding the cipher algorithm. The RSA algorithm is described in detail in its PKCS#1 documentation ( http://www.rsasecurity.com/rsalabs/pkcs/pkcs-1/index.html ).
The RSA algorithm was followed step-by-step in implementing the private methods such as RSADP , which performs the decryption of an integer that was encrypted with the RSA algorithm. I am not going step-by-step through the algorithm, simply because the code is exactly documented in each method following the PKCS#1, and an overview of RSA has already been provided. The example is a tested version for the readers to implement their own RSA encryptions.
The difference between the implementation in Listing 12-1 and other RSA algorithms that are provided by other Java Cryptography Extensions (JCE) is that the RSAPublicKey , RSAPrivateKey , and other RSA components that the JDK 1.4 supports can still be used. The implementation simply extends the JDK 1.4 to provide an RSA cipher. The JDK 1.4 already has support for RSA signature algorithms and RSA keys. The example code that tests the cipher, the javax.crypto.CipherSpi class, and the java.security.Provider class that loads the cipher as an SPI layer will be discussed in detail in the next chapter with other cipher algorithms. The purpose of the algorithm in this chapter is to demonstrate some of the differences between symmetric and asymmetric ciphers. Listing 12-1: The RichRSACipher class: An RSA cipher implementation
package com.richware.chap12; import java.io.*; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.security.*; import java.security.interfaces.*; import java.security.spec.*; import javax.crypto.*; import sun.misc.*; /** * Class RichRSACipher * Description: This is an example of a * simple RSA Encryption * RSA information is from PKCS#1v2.0 * a publication from RSA Security * * Copyright: Copyright (c) 2002 Wiley Publishing, Inc. * @author Rich Helton <rhelton@richware.com> * @version 1.0 * DISCLAIMER: Please refer to the disclaimer at the beginning of this book. */ public final class RichRSACipher extends CipherSpi { private RSAKeyGenParameterSpec params_; private SecureRandom random_; private final static boolean DEBUG = true; private int opmode_; private Key key_; private byte[] internal_buffer_; /** * Constructor RichRSACipher */ public RichRSACipher() {} /** * Method engineDoFinal * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected byte[] engineDoFinal( byte[] input, int inputOffset, int inputLen) throws IllegalBlockSizeException, BadPaddingException { byte[] output = engineUpdate(input, inputOffset, inputLen); internal_buffer_ = null; return output; } /** * Method engineDoFinal * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected int engineDoFinal( byte[] input, int inputOffset, int inputLen, byte[] output, int outputOffset) throws ShortBufferException, IllegalBlockSizeException, BadPaddingException { byte[] buffer; buffer = engineDoFinal(input, inputOffset, inputLen); if (output.length - outputOffset < buffer.length) { throw new ShortBufferException( "Output longer than buffer"); } System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, output, outputOffset, buffer.length); return buffer.length; } /** * Method engineGetBlockSize * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected int engineGetBlockSize() { if ((opmode_ == Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE) (opmode_ == Cipher.WRAP_MODE)) { return params_.getKeysize(); } else { return params_.getKeysize() - 1; } } /** * Method engineGetIV * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected byte[] engineGetIV() { return null; // If not supported } /** * Method engineGetKeySize * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected int engineGetKeySize(Key key) throws InvalidKeyException { /* * Get the key size based on bit length */ if (key instanceof RSAPrivateKey) { RSAPrivateKey k = (RSAPrivateKey) key; return k.getModulus().bitLength(); } else if (key instanceof RSAPublicKey) { RSAPublicKey k = (RSAPublicKey) key; return k.getModulus().bitLength(); } throw new InvalidKeyException("Unsupported RSA key!"); } /** * Method engineGetOutputSize * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected int engineGetOutputSize(int inputLen) { if ((opmode_ == Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE) (opmode_ == Cipher.WRAP_MODE)) { return params_.getKeysize(); } else { return params_.getKeysize() - 1; } } /** * Method engineGetParameters * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected AlgorithmParameters engineGetParameters() { return null; } /** * Method engineInit * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected void engineInit( int opmode, Key _key, AlgorithmParameterSpec params, SecureRandom _random) throws InvalidKeyException, InvalidAlgorithmParameterException { // Check for valid key if ((!(_key instanceof RSAPublicKey)) && (!(_key instanceof RSAPrivateKey))) { throw new InvalidKeyException("Unsupported RSA Key!"); } // Check for valid Parameter Spec if ((params != null) && (!(params instanceof RSAKeyGenParameterSpec))) { throw new InvalidAlgorithmParameterException( "Unsupported RSA AlgorithmParameterSpec!"); } // Initialize the params if (params != null) { params_ = (RSAKeyGenParameterSpec) params; } else { int keysize = 0; BigInteger publicExp = null; if (_key instanceof RSAPublicKey) { publicExp = ((RSAPublicKey) _key).getPublicExponent(); int modulusLength = ((RSAPublicKey) _key).getModulus().bitLength(); keysize = (modulusLength + 7) / 8; } else if (_key instanceof RSAPrivateKey) { int modulusLength = ((RSAPrivateKey) _key).getModulus().bitLength(); keysize = (modulusLength + 7) / 8; } if(DEBUG){ System.out.println("RichRSACipher:engineInit:keysize:" + keysize); } params_ = new RSAKeyGenParameterSpec(keysize, publicExp); } random_ = _random; // Check for valid types of opmode if ((opmode == Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE) (opmode == Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE) (opmode == Cipher.UNWRAP_MODE) (opmode == Cipher.WRAP_MODE)) { if (((opmode == Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE) (opmode == Cipher .UNWRAP_MODE)) && (_key instanceof RSAPublicKey)) { throw new InvalidKeyException( "Unsupported: Decrypt/UnWrap mode must use RSAPrivateKey"); } if (((opmode == Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE) (opmode == Cipher .WRAP_MODE)) && (_key instanceof RSAPrivateKey)) { throw new InvalidKeyException( "Unsupported: Encrypt/Wrap mode must use RSAPublicKey"); } if(DEBUG){ if ((opmode == Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE) (opmode == Cipher.UNWRAP_MODE)){ System.out.println("RichRSACipher:engineInit:DECRYPT_MODE"); }else{ System.out.println("RichRSACipher:engineInit:ENCRYPT_MODE"); } } } else { throw new InvalidKeyException("Unsupported opmode!"); } opmode_ = opmode; key_ = _key; } /** * Method engineInit * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected void engineInit( int opmode, Key _key, AlgorithmParameters params, SecureRandom _random) throws InvalidKeyException, InvalidAlgorithmParameterException { /* * Note _key is used instead of Key, because Key is a class. * Random is also a class. */ engineInit(opmode, _key, (AlgorithmParameterSpec) null, _random); } /** * Method engineInit * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected void engineInit( int opmode, Key _key, SecureRandom _random) throws InvalidKeyException { try { engineInit(opmode, _key, (AlgorithmParameterSpec) null, _random); } catch (InvalidAlgorithmParameterException ex) { throw new InvalidKeyException(ex.getMessage()); } } /** * Method engineSetMode * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected void engineSetMode(String mode) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { if (!mode.equalsIgnoreCase("ECB")) { throw new NoSuchAlgorithmException( "RSA supports only ECB mode"); } } /** * Method engineSetPadding * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected void engineSetPadding(String s) throws NoSuchPaddingException { // Only accepts avaliable padding if (!s.equalsIgnoreCase("PKCS1_V1_5")) { throw new NoSuchPaddingException("Unknown padding: " + s); } } /** * Method engineUpdate * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected byte[] engineUpdate(byte[] input, int inputOffset, int inputLen) { try { if (inputOffset > 0) { int outputSize = inputOffset + inputLen; byte[] tmp = new byte[outputSize]; System.arraycopy(input, inputOffset, internal_buffer_, internal_buffer_.length, inputLen); if ((opmode_ == Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE) (opmode_ == Cipher.WRAP_MODE)) { return (encrypt(internal_buffer_)); } else { return (decrypt(internal_buffer_)); } } else { internal_buffer_ = new byte[inputLen]; System.arraycopy(input, 0, internal_buffer_,0, inputLen); if ((opmode_ == Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE) (opmode_ == Cipher.WRAP_MODE)) { if(DEBUG){ System.out.println("RichRSACipher:engineUpdate:encrypting"); } return (encrypt(internal_buffer_)); } else { if(DEBUG){ System.out.println("RichRSACipher:engineUpdate:decrypting"); } return (decrypt(internal_buffer_)); } } } /* * Catches */ catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } return null; } /** * Method engineUpdate * Description: See CipherSpi */ protected int engineUpdate( byte[] input, int inputOffset, int inputLen, byte[] output, int outputOffset) throws ShortBufferException { byte[] buffer; buffer = engineUpdate(input, inputOffset, inputLen); if (output.length - outputOffset < buffer.length) { throw new ShortBufferException( "Output longer than buffer"); } System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, output, outputOffset, buffer.length); return buffer.length; } /** * Method I2OSP * Description: Integer to Octet String Primitive * See PKCS#1 */ private byte[] I2OSP(BigInteger x, int l) throws IllegalBlockSizeException { /* * Section 4.1 of PKCS#1v2.0 * I2OSP converts a nonnegative integer to an octet string * of a specified length. I2OSP (x, l) * Input: x nonnegative integer to be converted * l intended length of the resulting octet string * Output: X corresponding octet string of length l; or * integer too large * Steps: */ /* * 1. If x = 256l, output "integer too large " and stop. */ int j = (x.bitLength() + 7) / 8; if (l == -1) { l = j; } if ((j > l) (x.signum() == -1)) { throw new IllegalBlockSizeException("Block too large"); } /* * 2. Write the integer x in its unique l-digit representation * base 256: x = xl- 1 256^ (l- 1) + xl -2 256 256^(l -2) + ...& + x1 256 + x0 * where 0 = xi < 256 (note that one or more leading digits * will be zero if x < 256^ (l- 1)). */ byte[] C = x.toByteArray(); /* * remove the leading zeros */ int index = 0; for (; (index < C.length) && (C[index] == 0); index++); if (index > 0) { byte[] temp = new byte[C.length - index]; System.arraycopy(C, index, temp, 0, temp.length); C = temp; } else if (C.length > l) { throw new IllegalBlockSizeException("Block too large"); } /* * 3. Let the octet Xi have the value xl -i for 1 = i = l. * Output the octet string X = X1 X2 & ... Xl. */ if (C.length == l) { return C; } /* * C is not long enough */ byte[] result = new byte[l]; System.arraycopy(C, 0, result, l - C.length, C.length); return result; } /** * Method encrypt * Description: Encrypt with pad * See PKCS#1 * @param M the plaintext message */ private byte[] encrypt(byte[] M) throws IllegalBlockSizeException { /* * RSA Steps according to PKCS #1 v 2.0 pg 15 for encryption: * 1. Apply the EME-PKCS1-v1_5 encoding operation (Section 9.1.2.1) * to the message M to produce an encoded message EM of length k-1 * octets: EM = EME-PKCS1-V1_5-ENCODE (M, k-1) * If the encoding operation outputs "message too long, ," then output * message too long and stop. */ int k = params_.getKeysize(); byte[] EM = EME_PKCS1_V1_5_ENCODE(M, k - 1); /* * 2. Convert the encoded message EM to an integer message * representative m: m = OS2IP (EM) */ BigInteger m = new BigInteger(1, EM); /* * 3. Apply the RSAEP encryption primitive (Section 5.1.1) to the * public key (n, e) and the message representative m to produce * an integer ciphertext representative c: c = RSAEP ((n, e), m) */ BigInteger c = RSAEP((RSAPublicKey) key_, m); /* * 4. Convert the ciphertext representative c to a ciphertext C of * length k octets: C = I2OSP (c, k) */ byte[] C = I2OSP(c, k); /* * 5. Output the ciphertext C. */ return C; } /** * Method decrypt * Description: Decrypt with pad * See PKCS#1 * @param M the ciphertext message */ private byte[] decrypt(byte[] C) throws BadPaddingException, IllegalBlockSizeException { /* * RSA Steps according to PKCS #1 v 2.0 pg 16 for decryption: * 1. If the length of the ciphertext C is not k octets, output * decryption error and stop. */ int k = params_.getKeysize(); if (k != C.length) { throw new IllegalBlockSizeException("decryption error"); } /* * 2. Convert the ciphertext C to an integer ciphertext * representative c: c = OS2IP (C) */ BigInteger c = new BigInteger(1, C); /* * 3. Apply the RSADP decryption primitive to the private * key (n, d) and the ciphertext representative c to produce * an integer message representative m: m = RSADP ((n, d), c) * If RSADP outputs ciphertext out of range, then output * decryption error and stop. */ BigInteger m = RSADP((RSAPrivateKey) key_, c); /* * 4. Convert the message representative m to an encoded message * EM of length k-1 octets: EM = I2OSP (m, k-1) * If I2OSP outputs integer too large, then output decryption * error and stop. */ byte[] EM = I2OSP(m, k - 1); /* * 5. Apply the EME-PKCS1-v1_5 decoding operation to the encoded * message EM to recover a message M: M = EME-PKCS1-V1_5-DECODE(EM) * If the decoding operation outputs decoding error, then output * decryption error and stop. */ byte[] M = EME_PKCS1_V1_5_DECODE(EM); /* * 6. Output the message M. */ return M; } /** * Method EME_PKCS1_V1_5_ENCODE * Description: Pad encoding * * @param M the ciphertext message * @param emLen the length of encr message * * @return encoded pad * * @throws IllegalBlockSizeException * */ private byte[] EME_PKCS1_V1_5_ENCODE(byte[] M, int emLen) throws IllegalBlockSizeException { /* * Section 9.1.2.1 of PKCS#1v2.0 * 1. If the length of the message M is greater than emLen 10 * octets, output message too long and stop. */ if (M.length > emLen - 10) { throw new IllegalBlockSizeException("message too long"); } /* * 2. Generate an octet string PS of length emLen-M-2 * consisting of pseudorandomly generated nonzero octets. * The length of PS will be at least 8 octets. */ byte[] PS = new byte[(emLen - M.length - 2)]; // Fill the padding string with random non-zero bytes for (int i = 0; i < PS.length; i++) { PS[i] = (byte) (random_.nextInt(255) + 1); } /* * 3. Concatenate PS, the message M, and other padding to * form the encoded message EM as EM = 02 PS 00 M */ byte[] EM = new byte[emLen]; int index = 0; EM[index++] = (byte) 0x02; for (int i = 0; i < PS.length; i++) { EM[index++] = PS[i]; } EM[index++] = (byte) 0x00; for (int i = 0; i < M.length; i++) { EM[index++] = M[i]; } /* * 4. Output EM. */ return EM; } /** * Method EME_PKCS1_V1_5_DECODE * Description: Pad decoding * * @param EM the encrypted message * * @return pad * * @throws BadPaddingException * */ private byte[] EME_PKCS1_V1_5_DECODE(byte[] EM) throws BadPaddingException { /* * Section 9.1.2.2 of PKCS#1v2.0 * 1. If the length of the encoded * message EM is less than 10, output decoding error * and stop. */ if (EM.length < 10) { throw new BadPaddingException("message too short"); } /* * 2. Separate the encoded message EM into an octet string PS * consisting of nonzero octets and a message M as * EM = 02 PS 00 M. If the first octet of EM is not 02, * or if there is no 00 octet to separate PS from M, * output decoding error and stop. */ if (EM[0] != (byte) 0x02) { throw new BadPaddingException( "message not formatted properly"); } // Need to start by looking for the first non-zero byte int start = 0; while (EM[start] != (byte) 0x00) { start++; if (start >= EM.length) { throw new BadPaddingException("bad padding"); } } start++; // Ignore the first 00 /* * 3. If the length of PS is less than 8 octets, * output decoding error and stop. */ if (start < 10) { throw new BadPaddingException("bad padding"); } byte[] M = new byte[EM.length - start]; System.arraycopy(EM, start, M, 0, M.length); /* * 4. Output M. */ return M; } /** * Method RSEAP * Description: Performs the encryyrption * * @param publicKey the RSA public key * @param m the plaintext integer * * @return the ciphertext integer * * @throws IllegalBlockSizeException * */ private BigInteger RSAEP(RSAPublicKey publicKey, BigInteger m) throws IllegalBlockSizeException { /* * RSAEP ((n, e), m) * Input: (n, e) RSA public key * m message representative, an integer between 0 and n-1 * Output: c ciphertext representative, an integer between 0 and * n-1; or message representative out of range * Assumptions: public key (n, e) is valid */ BigInteger e = publicKey.getPublicExponent(); BigInteger n = publicKey.getModulus(); /* * 1. If the message representative m is not between 0 and n-1, * output message representative out of range and stop. */ BigInteger nMinusOne = n.subtract(BigInteger.ONE); /* * m > 0 and m < n-1 */ if (m.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO) < 0) { throw new IllegalBlockSizeException( "Ciphertext too small"); } if (m.compareTo(nMinusOne) > 0) { throw new IllegalBlockSizeException( "Ciphertext too large"); } /* * 2. Let c = me mod n. */ BigInteger c = m.modPow(e, n); /* * 3. Output c. */ return c; } /** * Method RSADP * Description: Performs the decryption * * @param K the RSA Private Key * @param c an integer representing * the cipher * * @return the plaintext integer * */ private BigInteger RSADP(RSAPrivateKey K, BigInteger c) { /* * RSADP (K, c) * Input: K RSA private key, where K has one of the following * forms: a pair (n, d) * a quintuple (p, q, dP, dQ, qInv) * c ciphertext representative, an integer between 0 and n-1 * Output: m message representative, an integer between 0 and n-1; or * ciphertext representative out of range * Assumptions: private key K is valid * Steps: * 1. If the ciphertext representative c is not between 0 and n-1, * output ciphertext representative out of range and stop. */ /* * 2.1 Let m = cd mod n. * PKCS #1 V2.0: RSA CRYPTOGRAPHY STANDARD 9 * Else, if the second form (p, q, dP, dQ, qInv) of K is used: */ if (!(K instanceof RSAPrivateCrtKey)) { BigInteger d = K.getPrivateExponent(); BigInteger n = K.getModulus(); BigInteger m = c.modPow(d, n); return m; } /* * 2. If the first form (n, d) of K is used: */ RSAPrivateCrtKey privateCrtKey = (RSAPrivateCrtKey) K; BigInteger p = privateCrtKey.getPrimeP(); BigInteger q = privateCrtKey.getPrimeQ(); BigInteger dP = privateCrtKey.getPrimeExponentP(); BigInteger dQ = privateCrtKey.getPrimeExponentQ(); BigInteger qInv = privateCrtKey.getCrtCoefficient(); /* * 2.2 Let m1 = cdP mod p. */ BigInteger m1 = c.modPow(dP, p); /* * 2.3 Let m2 = cdQ mod q. */ BigInteger m2 = c.modPow(dQ, q); /* * 2.4 Let h = qInv ( m1 m2 ) mod p. */ BigInteger h = m1.subtract(m2); h = h.multiply(qInv); h = h.mod(p); /* * 2.5 Let m = m2 + h q. */ BigInteger m = h.multiply(q); m = m.add(m2); /* * 3. Output m. */ return m; } }
One of the differences is the constant testing of the key. In the RSA case, the RSAPrivateKey is always associated and tested with the decryption mode. The RSAPublicKey is always associated with the encryption mode. In the symmetric key ciphers, there is only one key for all these methods. Another difference to note is that while the example is dictated to be ECB mode, it is different from other block ciphers. The engineGetBlockSize and engineGetOutputSize are associated with the key size. In most symmetric key algorithms, the cipher block size is different from the key size. A symmetric block size is related to the S-box, which might look more like a static 64-bit block. The RSA algorithm also has a padding string that adds delimiters to define where the pad begins and ends. An S-box in a symmetric algorithm will produce a ciphertext of a fixed size. The pad in this implementation will be of PKCS1_V1_5 type. The PKCS1_V1_5 is an older pad. This pad will put a padding string in the message to fill the pad to reach the key size. The padding string is just random bytes that act as a filler. A more secure pad evolved in the more current versions of RSA for padding as the Optimal Asymmetric Encryption Padding (OAEP). The OAEP will XOR the plaintext. For the padding, it will apply a message digest and a mask generation function (MGF). The MGF will mask the pad so that it is difficult to tell what is pad and what is data for encryption. The OAEP prevents parsing from the delimiters that can be looked at to determine what is message and what is pad. Simply put, because the asymmetric algorithm is very key-size-centric, it must pad differently than the block ciphers. Many of the block ciphers will pad using PKCS#5 of the RSA documentation. The PKCS#5 padding will pad a number at the end that describes the number of padded bytes before encryption. If 8 bytes need to be padded at the end of the plaintext, the algorithm will input the number 8 in the last 8 byes. See Figure 12-7 for a comparison. Which key is used in the asymmetric algorithm decides whether the encryption mode or decryption mode is set. The asymmetric cipher depends on the discrete logarithm problem, mentioned in previous chapters, and works with integers instead of a pure S-box implementation. 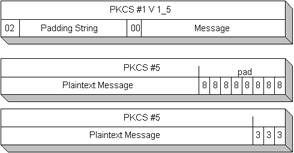 Figure 12-7: Padding in ciphers
Java Security Solutions ISBN: 0764549286
EAN: 2147483647 Year: 2001
Pages: 222 Authors: Rich Helton, Johennie Helton
flylib.com © 2008-2017. If you may any questions please contact us: flylib@qtcs.net |