13.5 Switched Network Use for Overcoming Congestion
13.5 Switched Network Use for Overcoming Congestion
One problem frequently encountered by network designers, managers, and analysts is determining the operating rate of a WAN transmission facility. Almost all WAN transmission facilities are either leased analog or digital lines whose monthly cost is proportional to the data transmission rate they provide. Most organizations typically attempt to determine their busy-hour traffic and obtain a WAN transmission facility that provides an acceptable level of performance during the busy-hour. While this is a valid network design technique, it neither considers the use of a new class of equipment known as bandwidth-on-demand inverse multiplexers (BODIMs) nor the fact that in many organizations busy- hour transmission may considerably exceed normal transmission.
13.5.1 Using Bandwidth-on-Demand Inverse Multiplexers
To illustrate the use of bandwidth-on-demand inverse multiplexers (BODIMs), as well as a feature known as dial-on congestion incorporated into some remote bridges and routers, we need an example. Thus, let us assume that the network analysts determined that a fractional T1 line operating at 128 Kbps was required to interconnect two remote bridges at a cost of $4500 per month. Also assume that the cost of switched 56-Kbps transmission is $30 per hour. Further assume that during an eight-hour day, the WAN facility only requires 128 Kbps of bandwidth for 90 minutes, while the remainder of the workday , a bandwidth of 64 Kbps or less provides an acceptable level of performance.
Figure 13.6 illustrates the use of BODIMs that examine the flow of packets between remote bridges. As the flow of packets increases to the point where there is essentially no available bandwidth on the leased line for a predefined period of time, the multiplexer initiates a switched 56-Kbps call to the distant multiplexer. Based on our assumed cost of $30 per hour, switched 56-Kbps transmission for 90 minutes per day would result in a daily cost of $45, or $990 if there are 22 working days in the month. If a 64-Kbps fractional T1 line costs $2800 per month, the total cost of using a 64-Kbps leased line and supplementing its capacity via the use of switched 56-Kbps service would be $3790, not including the cost of the bandwidth-on-demand inverse multiplexers. Thus, in this example, the use of BODIM equipment would result in a monthly line cost reduction of $710.
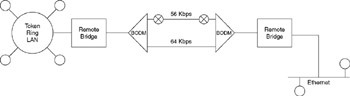
Figure 13.6: Using Bandwidth-on-Demand Inverse Multiplexers
13.5.2 Dial-On Congestion
To alleviate the cost of separate bandwidth-on-demand inverse multiplexers, several vendors manufacturing remote bridges and routers have incorporated a dial-on-congestion capability into their products. This feature results in the use of a second port on a remote bridge or router for switched dial use during peak periods of activity
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 111