File Formats Explained
| There are too many file formats to ignore. Unfortunately, each industry is different; 3D animators need different images than magazine designers. A brief overview of file types will be useful to identify the formats that you will need. Then just revisit this chapter when you need to brush up on a new format. Photoshop (.psd)
Photoshop format is the default file format. This format supports all of Photoshop's features. It's a good idea to save your design files in this format for maximum editability. Additionally, many other software packages recognize Photoshop layers. Alias Pix (.pix)Optional Plug-in
Alias is a 3D software company best known for the Maya animation software. Some of its software tools use the file format PIX for individual images. From the Save As dialog box, you can select from several file formats. Certain ones may be unavailable due to bit depth or image mode. 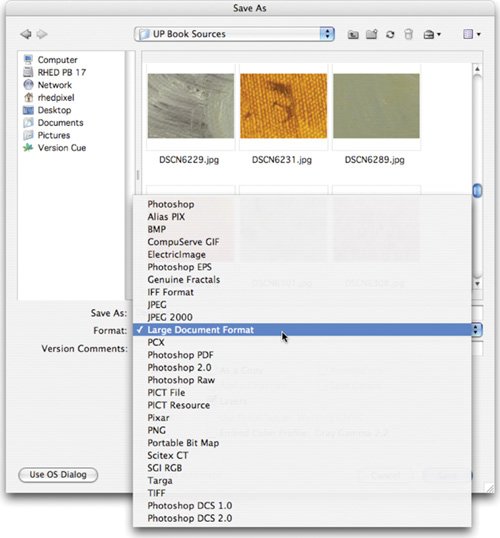 BMP (.bmp)
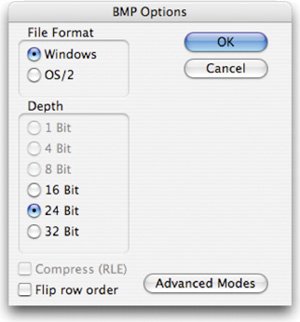
When saving a BMP file, you have several options available. These options optimize the file for use with other applications. Microsoft Paint's BMP is a standard Windows image format on DOS and Windows computers. The BMP format supports RGB, Indexed Color, Grayscale, and Bitmap color modes. The BMP format supports several lower-quality modes and is most used by video game developers. Cineon (.cin or .dpx)
Cineon is a common file format for digital film work and is used in the motion picture industry. It is a subset of the ANSI/SMPTE DPX file format, which represents each color channel of a scanned film negative in a "10-bit log" format. Photoshop does not have a 10-bit space, so instead handles the images in 16-bit mode. The DPX file format is derived from the output file format of the Kodak Cineon film scanner. The Cineon format has been replaced by a related format called DPX. CompuServe GIF (.gif)
Online service provider CompuServe originally developed the Graphics Interchange Format (GIF). This format displays 8-bit or indexed-color graphics and images in HTML documents on the Internet. You'll hear the file called both "giff" and "jiff"; both are acceptable. GIFs use a color table (with no more than 256 colors) to represent the image. This can lead to a small file size, but also banding in the image. If you need transparency in a Web graphic, GIF is one of two choices (the other is PNG). There are also animated GIFs, which are GIF frames displayed one after the other to create animation. Unless you need transparency or animation, JPEG is a better option for Web delivery. Compare a JPEG (left)and a GIF (right). Notice how the GIF uses fewer colors. This format can reduce file size, but often creates banding or color shifts.  ElectricImage (.img)Optional Plug-in
This is a very uncommon file format associated with animation software from Electric Image. Photoshop EPS (.eps)
You can embed an image preview into an EPS file, which makes previewing your image easier in a page-layout program. The Encapsulated PostScript (EPS) language file format can contain both vector and bitmap graphics. It is nearly universal and is supported by virtually all graphics, illustration, and page-layout programs. EPS format is used to transfer PostScript artwork between applications. When you open an EPS file that contains vector graphics, Photoshop rasterizes the image. Filmstrip (.flm)
The Filmstrip format is used for movie files created by Adobe Premiere and Premiere Pro. Every frame of video is saved to one file, which you can open in Photoshop for Rotoscoping (painting on video or film frame-by-frame). If you change resolution, delete alpha channels, or alter the color mode, you won't be able to save it back to Filmstrip format. This format is becoming much less common as most users turn to After Effects for this sort of work. Genuine Fractals (.stn)Third-Party Plug-in
While the Genuine Fractals plug-in is a third-party product (and costs extra), it is so common in certain industries that it bears mention. Most versions of the plug-in write to the .stn format (often called Sting). There are two versions of Genuine Fractals: one that supports only RGB images and a Pro version that adds CMYK and Lab support. The major benefit of the format is that an image can be saved as an .stn file, then scaled up to 800% larger. While some image degradation occurs, it is much less than what Photoshop would cause by upsampling. The file format also allows for large amounts of visually lossless compression to reduce file size. This format is very common in the large format print industry (such as billboards or product displays). IFF Format (.iff)Optional Plug-in
Most of you reading this book are too young to remember Commodore computers. The manufacturer produced computers between 1976 and 1994 and is often remembered for the Commodore 64, which was a very successful personal computer in the early days of computing. A follow-up computer was the Commodore Amiga. The Amiga Interchange File Format (IFF) is the standard raster file format for the Commodore Amiga. You can use this format to transfer images between the Macintosh/Windows systems and Amiga computers. You'll also occasionally see this format used in animation programs. Some paint programs on IBM computers also support this format. RGB, Indexed Color, Grayscale, and Bitmapped modes can be saved in this format. Besides supporting Amiga output, the file can also export for Maya. JPEG (.jpg)
The Joint Photographic Experts Group ( JPEG) format is most often used to display continuous-tone images (such as photos) on the Internet. Most digital cameras use JPEG as it provides excellent compression; the maximum setting provides comparable quality to much larger files. Occasionally the print industry (especially newspapers) will use JPEGs. Notice the difference in file-size savings between the two formats. The JPEG (even at maximum quality) is almost nine times smaller. File savings make JPEG a popular format for digital cameras and the newspaper industry. 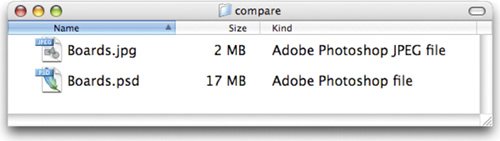 The JPEG format supports RGB, CMYK, and Grayscale color modes, but does not support alpha channels. JPEG is a lossy compression, which means that some data is discarded during compression of the image. JPEGs should not be used as an archive or production file format. You should generally only save JPEG files once, as resaving continues to discard data and lower image quality. If you are using it as a source format, be sure to set the digital camera to Maximum quality. The best way to create JPEGs for the Internet is with the Save For Web command (discussed in depth at the end of this chapter). JPEG 2000 (.jpf)Optional Plug-in
The JPEG 2000 format is a significant improvement upon the JPEG standard. It offers more options and greater flexibility, and is designed for use by the Web and print publishing industries (although the video and film industry is examining it as well). Not all Web browsers support the JPEG 2000 format natively and may require a plug-in. While traditional JPEG files use lossy compression, the JPEG 2000 format supports optional lossless compression. It can also work in 16-bit mode for greater color fidelity and retain transparency, alpha channels, and spot color channels. In fact, by using an alpha channel, you can specify a region of interest. This area will have more details preserved while the rest of the image can have greater compression (which reduces file size). The JPEG 2000 dialog box offers significantly greater control over image compression than the standard JPEG format. 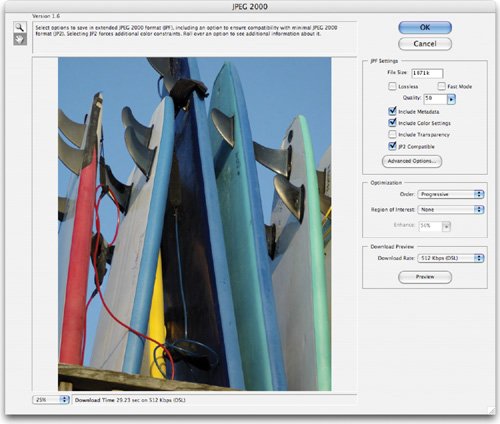 Large Document Format (.psb)
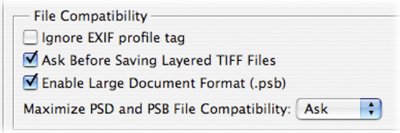
The two file formats are virtually identical. Using the Large Document Format does not increase file size, it just allows a larger sized file to be saved. There is normally a 2 GB file size limit in older versions of Photoshop and most other computer applications. To respond to the need for larger file sizes, Adobe launched the Large Document Format (PSB). It supports documents up to 300,000 pixels in any dimension (up to 100 inches at 300 ppi). All Photoshop features, such as layers, effects, and filters, are supported. Additionally, 32-bits-per-channel images can be saved as PSB files. It's important to remember that files saved in the PSB format can be opened only in Photoshop CS or Photoshop CS2. Other applications and earlier versions of Photoshop cannot open documents saved in PSB format. Also, to save a document as a PSB file, the Enable Large Document Format option must be enabled in your Preferences. OpenEXR (.exr)
OpenEXR is a specialized file format used by the visual effects industry for high dynamic range images. It was developed by Industrial Light and Magic and released under an open source license. The format supports multiple lossless or lossy compression methods. It is designed to support both 16-bit and 32-bit images (although Photoshop currently supports only 32-bit images). Its primary benefit is that it allows for over 30 stops of exposure (which gives it incredible range of light to dark). For much more information, see www.openexr.com/about.html. PC Paintbrush (.pcx)
PC-compatible computers can use the PC Paintbrush format. The format is designed to match the standard VGA color palette. PCX supports RGB, Indexed Color, Grayscale, and Bitmap color modes, but does not support alpha channels. It is most often a compressed file and supports bit depths of 1, 4, 8, or 24. Because of its small color range and compressed images, this format is not very useful. Photoshop PDF (.pdf)
The Portable Document Format is a cross-platform, cross-application file format. PDF files are designed to accurately display and preserve fonts, page layouts, and both vector and bitmap graphics. You can also transfer Photoshop's annotation notes (both text and audio) into a PDF. The PDF dialog box allows for several options including security. This allows you to password-protect a file from opening or being modified. 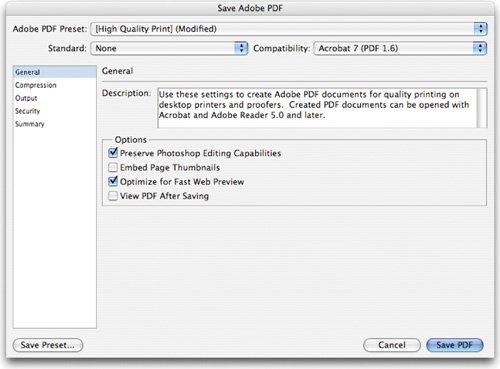 The Photoshop PDF format is the only PDF that Photoshop can save and it's a hybrid. It supports layers and other Photoshop features, but not all PDF features. You do have several choices, though, in the Save Adobe PDF dialog box (including password and permissions). You do not need to flatten to save a PDF file. This file can then be transferred to coworkers or clients for review and comment using Adobe Acrobat or viewed using the free Adobe Reader. This is an excellent format for review purposes.
Photoshop 2.0
File this format under the "just-in-case" category. If you need to send a file for use in Photoshop 2.0, choose to export to this format. It will only allow you to save a copy and all layer information will be discarded. Occasionally, some third-party software application may require a Photoshop 2.0 file; however, this file format is fairly obsolete. Photoshop Raw (.raw)
The raw format is a flexible file format for transferring files between applications and computer platforms. Essentially, a text file is written containing a stream of bytes describing the color information for the image. Every pixel is described in binary format. It's important to note that a Photoshop raw image is not in the same file format as a camera raw image. Most users can completely avoid this format. PICT File (.pct)
The Macintosh Picture format is widely used by video editors who initially grew up on Macintosh-based editing systems. Its popularity can be traced back to many software packages, which historically required graphics to be in the PICT format. The PICT format is very effective at compressing large areas of solid color. This compression results in a huge file savings for alpha channels, which are mostly black or white. On the Mac platform, you have choices of additional JPEG compression. Avoid these as they cause import problems on PCs, and the file-size savings are not worth the quality loss.
PICT Resource (.rsr)
The PICT resource is a PICT file that is contained in a Mac OS file's resource fork. This format is often used to create startup screens for software. While similar to a plain PICT file, you can avoid it if you are not doing software programming. You can edit a PICT resource file by importing it into Photoshop. Pixar (.pxr)
The Pixar format is designed for high-end 3D applications (yes, Pixar makes movies and software). It supports RGB and grayscale images with a single alpha channel. If you create 3D animation, you may use this format for integration with third-party programs. PNG (.png)
The Portable Network Graphics format provides lossless compression. It is increasingly common on the Internet, but not all browsers support it. The PNG format was created to be a patent-free alternative to GIF. Its major advantage is the PNG-24 file, which allows for 24-bit images (8 bits per channel) and embedded transparency. It is technically superior to GIF. The file on the left is a PNG. Notice how the transparency is handled perfectly (even in the soft glowing areas). On the right is a GIF, which is an 8-bit image. Transparency is not handled as cleanly, and you will notice a white edge outside of the glow. Portable Bit Map (.pbm)
This format is designed for lossless data transfer between many different applications. The Portable Bit Map (PBM) file format is also known as Portable Bitmap Library or Portable Binary Map. It supports monochrome bitmaps (1 bit per pixel). The Portable Bit Map format functions as the common language of a large family of bitmap conversion filters including Portable FloatMap (PFM), Portable Graymap (PGM), Portable Pixmap (PPM), and Portable Anymap (PNM). This format can be used to store floating-point images that can be used for 32-bits-per-channel HDR files. QuickTime Movie (.mov)
The QuickTime Movie format is a cross-platform format developed by Apple. It is used for time-based media, such as video. As of Photoshop CS2, only ImageReady allows for the opening (and saving) of QuickTime movies. Radiance (.hdr)
Installing QuickTime is beneficial to Photoshop. By default it's on Macintosh systems, but it's a free download for Windows (www.quicktime.com). Having QuickTime installed unlocks more file formats. The Radiance format is another High Dynamic Range (HDR) image format. It allows for 32-bits-per-channel, which produces superior manipulation of exposure. This format was originally developed for the Radiance system. This is a high-end professional tool for visualizing lighting in virtual environments. The file format stores the quantity of light per pixel (not just the colors) to be displayed onscreen. Radiance (HDR) files are often used in 3D modeling. Scitex CT (.sct)
The Scitex Continuous Tone format is used for high-end print work on Scitex computers. This format needs special scanners and rasterizing formats, and is designed for output of high-quality print such as magazines and art prints. CMYK images saved in Scitex CT format can have extremely large file sizes. By using Scitex systems, a professional printer can produce images with very few moiré patterns. While Photoshop can create a Scitex CT file, you'll need specialized software to transfer it to a Scitex system. SGI RGB (.sgi)Optional Plug-in
The SGI RGB format is a somewhat uncommon file format that often appears in the computer graphics and simulation industry. The format was originally developed for use on SGI systems. Softimage (.pic)Optional Plug-in
Softimage creates professional 3D animation and modeling software. This optional plug-in allows for increased compatibility with Softimage's tools. SWF (.swf)
The SWF format is a very popular Web format that is optimized for playing vector-based animations developed by Macromedia. SWF is pronounced "swiff" and the file extension was based on the original player Shockwave. Several programs can author SWF files, but the most popular is Macromedia Flash. While optimized for vector playback, the format does support raster-based files. The SWF format is a streaming format. This means that the file plays as soon as enough of the file has downloaded. SWF files currently can only be written from ImageReady. Adobe recently purchased Macromedia, and users are hopeful for tighter Flash and SWF integration. Targa (.tga)
The Targa format was originally designed for use on systems using the Truevision video board. The name is in fact an acronym meaning Truevision Advanced Raster Graphics Adapter. The Targa format predates Photoshop. It is a common format in the video industry (as it supports alpha channels), especially for PC users. TIFF (.tif)
The Tagged-Image File Format is one of the most common and flexible formats available. It is widely used to exchange files between applications and computer platforms, and has a long legacy of compatibility. Older programs capped TIFF files at 2 GB, but starting with Photoshop CS, this barrier was changed to 4 GB. One benefit of TIFF is that it acts as a layered file within Photoshop, but is treated as a flattened file by other applications. Additionally, TIFF is the one of the few formats to work in a bit depth of 8, 16, or 32 bits per channel. High dynamic range images can be saved as 32-bits-per-channel TIFF files. In the File Handling preferences you can modify how layered TIFFs are handled. While there, you can also turn on support for the Large Document Format. Wavefront RLA (.rla)Optional Plug-in
The Wavefront RLA format was designed to work with the Wavefront Data Visualizer. This is a scientific visualization package for volumetric data. While these systems are for high-end purposes, you may need to provide data to them. Wireless Bitmap (.wbm)
This is the standard format for images on mobile devices such as cell phones. It is an optimized format, but only supports 1-bit color. This means that WBMP images contain only black and white pixels. The file format can only be accessed by choosing the Save For Web command. Photoshop DCS 1.0 and 2.0 (.eps)
The Photoshop DCS format is an adoption of the Desktop Color Separations (DCS) format (a version of EPS developed by Quarkmaker of page-layout software.) The original DCS format is referred to as DCS 1.0, but the more flexible format (referred to as DCS 2.0) allows for exporting images containing spot channels. The format is primarily intended for professional printing of CMYK images. To print DCS files, you must use a PostScript printer. Adobe Digital Negative (.dng)
There are several competing raw file formats for digital cameras (most are proprietary to a particular manufacturer.) Adobe released the Adobe Digital Negative (DNG) file format to unify things. The concern is that proprietary formats will become obsolete more quickly due to company changes. The DNG format hopes to be the open standard model. The specs for this format are available to camera and software manufacturers, and Adobe has had relative success getting others to adopt it. For more information, visit www.adobe.com/dng. The DNG format offers a unified solution for camera raw images. You can only save a DNG file from the Adobe Camera Raw dialog box. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 129