The XPath Data Model
| An XPath query operates on a namespace well- formed XML document after it has been parsed into a tree structure. The particular tree model XPath uses divides each XML document into seven kinds of nodes:
The XPath data model does not include entity references, CDATA sections, or the document type declaration. Entity references are resolved into their component text and elements. CDATA sections are treated the same as any other text, and will be merged with any adjacent text before a text node is formed. Default attributes are applied, but otherwise the document type declaration is not considered . In the XPath data model, each node has a string value. Furthermore, attributes, elements, processing instructions, and namespace nodes have expanded names, which are divided into a local part and a namespace URI. Table 16.1 summarizes XPath's rules for calculating names and values for its seven node types. Table 16.1. XPath Expanded Names and String Values
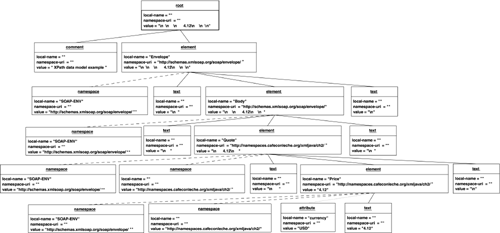
If an XPath function such as local-name() or namespace-uri() attempts to retrieve the value of one of these properties for a node that doesn't have that property, then it returns the empty string. An example and a diagram should help explain this. Consider the simple SOAP response document in Example 16.2. Example 16.2 A SOAP Response Document<?xml version="1.0"?> <!-- XPath data model example --> <SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" /> <SOAP-ENV:Body> <Quote xmlns="http://namespaces.cafeconleche.org/xmljava/ch2/"> <Price currency="USD">4.12</Price> </Quote> </SOAP-ENV:Body> </SOAP-ENV:Envelope> Figure 16.2 is a UML object diagram that identifies the properties of the different XPath nodes in this document and the connections between them. Solid lines indicate a child relationship. Dashed and dotted lines indicate namespace and attribute connections, respectively. Document order runs from top to bottom and left to right (although the exact order of namespace nodes and attribute nodes attached to the same element is implementation dependent). Line breaks are indicated by \n in this figure. Note that white space is significant in the XPath data model. Figure 16.2. An XPath Data Model |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 191
- Chapter IV How Consumers Think About Interactive Aspects of Web Advertising
- Chapter VI Web Site Quality and Usability in E-Commerce
- Chapter VII Objective and Perceived Complexity and Their Impacts on Internet Communication
- Chapter XI User Satisfaction with Web Portals: An Empirical Study
- Chapter XIII Shopping Agent Web Sites: A Comparative Shopping Environment